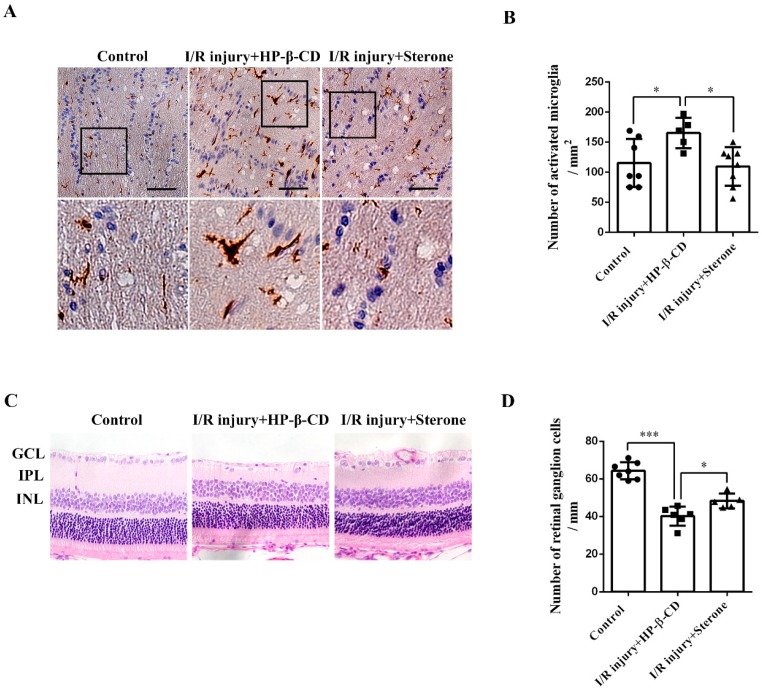
Figure 4.
Sterone inhibited the microglial activation and retinal RGCs loss induced by ischemia/reperfusion injury in the rat AIH model. The rat AIH model was performed by retinal ischemia for 60 min, followed by sterone (80 μg/eye) treatment for 30 s and retinal reperfusion for 48 h. Microglial activation in the optic nerves was determined using Iba-1 immunohistochemistry. The immunohistochemistry results were presented in microphotographs (A) and statistical graphs (B). (A,B), n (Control) = 7, n (I/R injury+HP-β-CD) = 5, n (I/R injury+Sterone) = 8. RGCs survival was determined using light microscopic analysis. Microphotographs were obtained in (C) and the number of RGCs was quantified in (D). GCL, retinal ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer. (C,D), n (Control) = 7, n (I/R injury+HP-β-CD) = 6, n (I/R injury+Sterone) = 5. Scale bars, 50 μm. * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001.