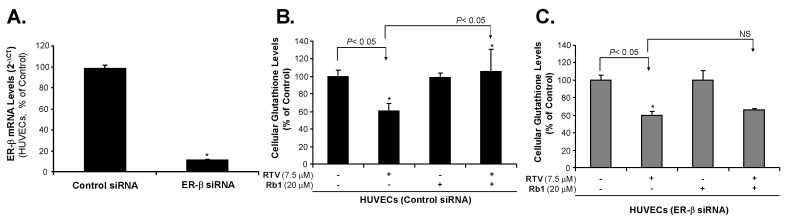
Figure 3.
Effect of ER-β silencing, ritonavir (RTV), and ginsenoside Rb1 on ROS levels in HUVECs. (A) Effect of ER-β silencing on ER-β mRNA (real time PCR). ER-β silencing was achieved with specific oligonucleatide siRNA as compared with a scramble siRNA as a negative control (100%); (B) Cellular glutathione (GSH) levels in HUVECs treated with control siRNA. The results of the cellular GSH assay are inversely proportional to reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels. Cellular glutathione levels were standardized with untreated control cells as 100%. RTV treatment decreased cellular GSH levels, indicating oxidative stress. Ginsenoside Rb1 blocked the effect of RTV in HUVECs treated with control siRNA; (C) Cellular glutathione (GSH) levels in HUVECs treated with ER-β siRNA. RTV treatment decreased cellular GSH levels, while ginsenoside Rb1 did not block the effect of RTV in HUVECs in which ER-β had been silenced. Student’s t-test was used to compare the control with the treated cells or between two groups. * p < 0.05. n = 3/group. siRNA (small interfering RNA).