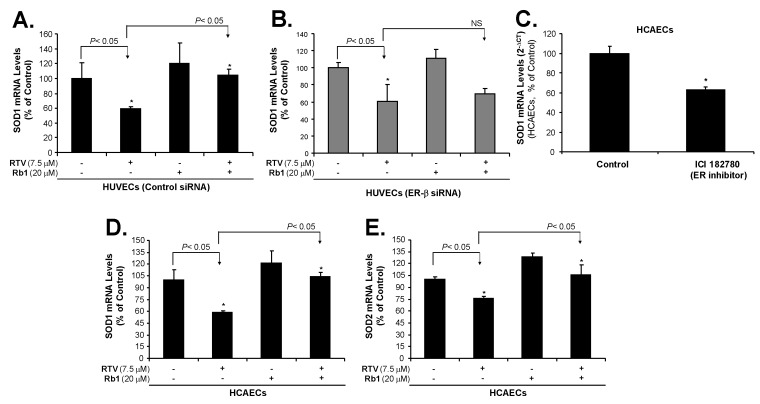
Figure 4.
Effect of ER-β silencing, ritonavir (RTV), and ginsenoside Rb1 on the mRNA levels of SOD1 and SOD2 (real time PCR). (A) RTV treatment decreased SOD1 mRNA levels, and ginsenoside Rb1 effectively blocked this effect of RTV in HUVECs with control siRNA; (B) RTV treatment decreased SOD1 mRNA levels, while Rb1 did not block RTV-induced reduction of SOD1 mRNA levels in HUVECs in which ER-β had been silenced; (C) HCAECs were treated with ER inhibitor ICI 182780 (10−6 M) or DMSO (negative control) for 24 h, SOD1 mRNA levels were decreased in the ICI-treated group compared with control group, showing a critical role of ER on the maintenance of SOD1 levels; (D) RTV treatment decreased SOD1 mRNA levels, and ginsenoside Rb1 effectively blocked this effect of RTV in HCAECs; (E) RTV treatment decreased SOD2 mRNA levels, and ginsenoside Rb1 effectively blocked this effect of RTV in HCAECs. Student’s t-test was used to compare the control with the treated groups or between two groups. n = 3, * p < 0.05.