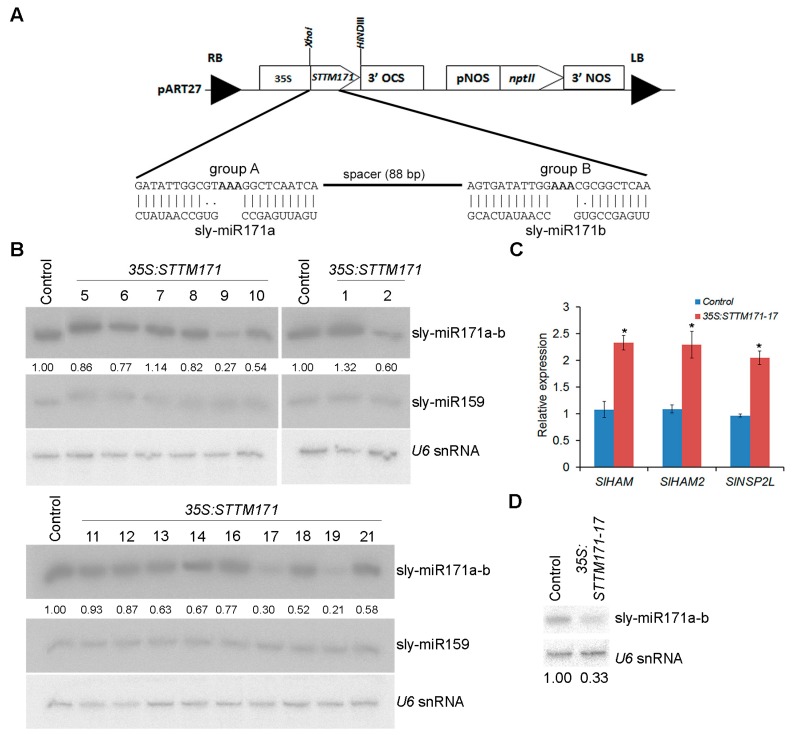
Figure 2.
Generation of transgenic STTM171 tomato with reduced sly-miR171 levels. (A) A scheme of the Short Tandem Target Mimic construct used for tomato M82 transformation. The Watson–Crick pairings between group A and B target mimic sites and sly-miR171 representative members are shown in the expanded region. (B) RNA gel blot analysis of sly-miR171 levels in indicated transgenic T0 plants. Total RNA (5 µg) from leaves was probed by sly-miR171a (sly-miR171a-b), sly-miR159 and U6 antisense probes. Sly-miR171 expression levels were determined after normalization to sly-miR159 and U6 snRNA by geometric averaging and are indicated below. (C) RT-qPCR analysis of sly-miR171 target transcripts in RNA from young leaves of one-month old T2 35S:STTM171-17 plants. TIP41 expression values were used for normalization. Error bars indicate ± SD of three biological replicates, each measured in triplicate. Asterisks indicate significant difference relative to 35:GFP control plants (Tukey–Kramer multiple comparison test; p < 0.01). (D) RNA gel blot analysis of sly-miR171 in 5 µg total RNA from the samples analyzed in C. The blots were probed with sly-miR171a (sly-miR171a-b) antisense probe. Sly-miR171 expression levels were determined after normalization to U6 snRNA and are indicated below.