Figure 1.
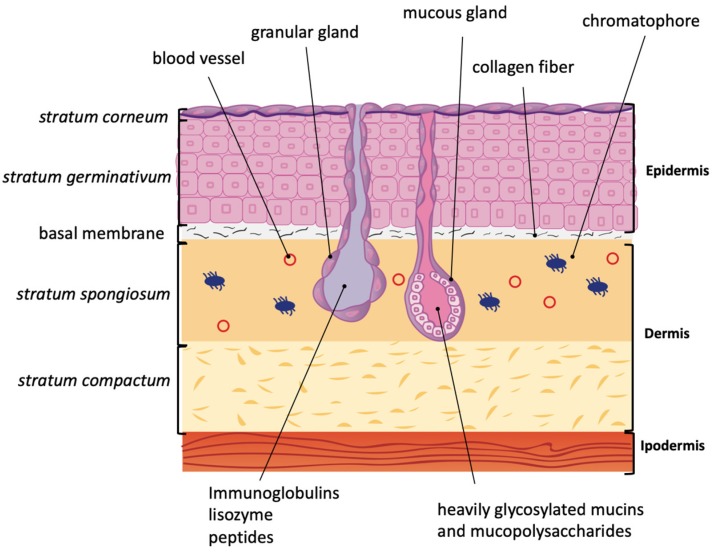
Amphibian skin anatomy. Amphibian epidermis is composed of the stratum corneum (only one layer of keratinized cells) followed by a regenerative basal layer, the stratum germinativum. These two layers are separated by irregular intracellular spaces that are interrupted by desmosomes. The stratum germinativum is usually 4–8 cell thick, with a progressive changing of shape from columnar to shorter from the innermost layer to the outermost. Collagen fibers reach basal membrane and separate epidermis from dermis. The latter is formed by stratum spongiosum and stratum compactum. In the stratum spongiosum, granular and mucous glands are present. Chromatophores, responsible of multi-colored amphibian skin, are also present in the dermis.