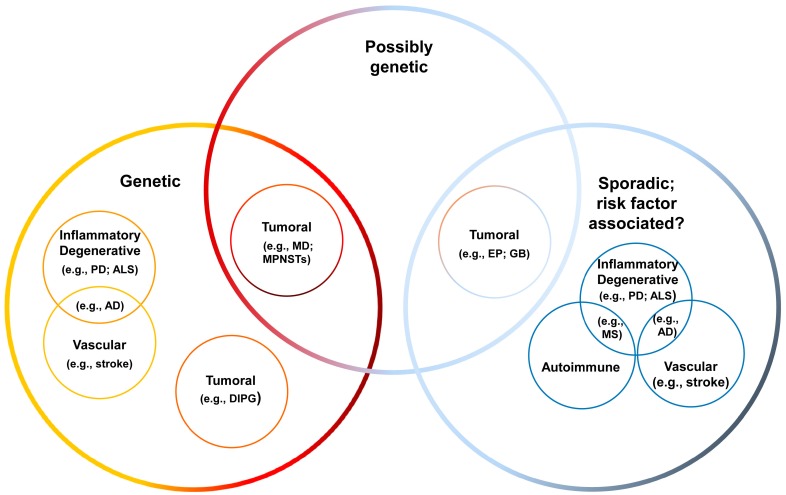
Figure 3.
Diagrammatic representation of the various groups encompassing the neurological diseases presented in Table 1. It can be seen that according to their main etiopathogenic feature, neurological diseases can be classified into distinct groups. However, there are various examples in which a disease can be classified into more than one group because the etiopathogenic features are mixed, or incompletely understood. Abbreviations: AD, Alzheimer’s disease; ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; DIPG, diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas; EP, ependymoma; GB, glioblastoma; MB, medulloblastoma; MPNSTs, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors; MS, multiple sclerosis; PD, Parkinson’s disease.