Table 5.
Antimicrobial activity of natural caged xanthones with pyran group.
| No. | Name/Structure | a | Antimicrobial Activity (MIC or Zone of Growth) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 37N | Hanburinone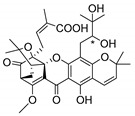
|
−62° (0.09) | MRSA (200 µM) |
| 38N | Isomoreollin B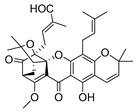
|
−44° (0.11) | MRSA (200 µM) |
| 39N | Morellin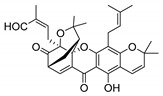
|
−600° (0.04) | MRSA (200 µM) |
| 40N | Moreollic acid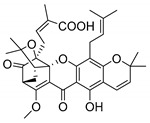
|
−39° (0.22) | MRSA (25 µM) |
| 41N | Morellic acid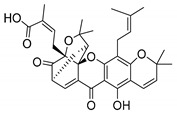
|
−541° (0.19) | MRSA (25 µM); MRSA USA300 SF8300 (19.52 mmb; 12.5 µM); MSSA ATCC 25923 (19.23 mm b; 12.5 µM) |
| 42N | Deoxymorellin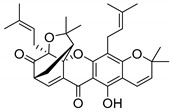
|
MRSA USA300 SF8300 (6 mm b); MSSA ATCC 25923 (6 mm b) | |
| 43N | Isomorellinol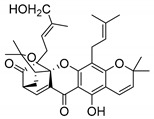
|
MRSA USA300 SF8300 (8.57 mm b); MSSA ATCC 25923 (7.75 mm b) | |
| 44N | Gambogic acid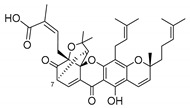
|
(0.17) = −714.1° | MRSA USA300 SF8300 (17.29 mm b; 25 µM); MSSA ATCC 25923 (16.59 mm b; 12.5 µM) |
MIC: Minimum inhibitory concentration; MRSA: Methicillin-resistant S. aureus; MSSA: Methicillin-sensitive S. aureus; a Specific rotation measured in CHCl3; b The antimicrobial studies were determined using the disc diffusion method, where the inhibitory growth zones’ inhibition caused by the tested compounds is expressed in millimeters.
