Table 10.
Antimicrobial activity of α-mangostin analogues.
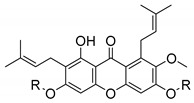
| No. | Structure/R | Antimicrobial Activity (MIC) |
|---|---|---|
| 32S |
|
S. aureaus (6 µg/mL); MRSA DM21455 (12 µg/mL); MRSA DM09809R (6 µg/mL); B. cereus ATCC 11778 (12 µg/mL) |
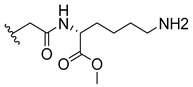
| 33S |
|
S. aureaus (>50 µg/mL); MRSA DM21455 (>50 µg/mL); MRSA DM09809R (>50 µg/mL); B. cereus ATCC 11778 (>50 µg/mL); Mycobacetrium smegmatis (>24.9 µg/mL); M. bovis (>24.9 µg/mL) |
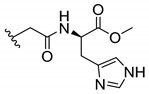
| 34S |
|
S. aureaus DM4001 (2 µg/mL); MRSA DM21455 (3 µg/mL); MRSA DM09809R (3 µg/mL); B. cereus ATCC 11778 (2 µg/mL); M. smegmatis (>25.1 µg/mL); M. bovis (>25.1 µg/mL); MSSA (7 strains) (2–4 µg/mL); VISA (4 µg/mL); MRSA (10 strains) (2-4 µg/mL); EMRSA (3 strains) (2–4 µg/mL); teicoplanin-RI (2 µg/mL); MDR (2 µg/mL); Staphylococcus epidermidis (2 strains) (2 µg/mL); VSE (3 strains) (2–4 µg/mL); VRE (5 strains) (2–4 µg/mL); Streptococcus (4 strains) (4–8 µg/mL); Corynebacterium jeikeium and L. monocytogenes (4–8 µg/mL) |
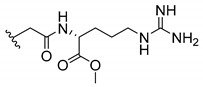
| 35S |
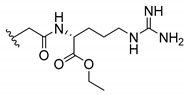
|
S. aureaus (6 µg/mL); MRSA DM21455 (6 µg/mL); MRSA DM09809R (12 µg/mL). B. cereus ATCC 11778 (12 µg/mL) |
| 36S |
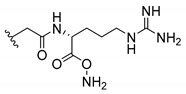
|
S. aureaus DM4001 (6 µg/mL); MRSA DM21455 (1 µg/mL); MRSA DM09809R (6 µg/mL); B. cereus ATCC 11778 (6 µg/mL); M. smegmatis (>26.1 µg/mL); M. bovis (>11.1 µg/mL) |
| 37S |
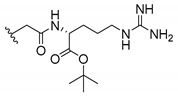
|
S. aureaus (12 µg/mL); MRSA DM21455 (12 µg/mL); MRSA DM09809R (12 µg/mL). B. cereus ATCC 11778 (12 µg/mL) |
| 38S |
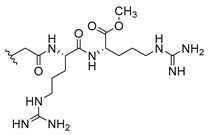
|
S. aureaus (0.5 µg/mL); MRSA DM21455 (2 µg/mL); MRSA DM09809R (3 µg/mL); B. cereus ATCC 11778 (3 µg/mL); MSSA (7 strains) 2–4; VISA 2; MRSA (10 strains) (2 µM); EMRSA (3 strains) (2 µM); teicoplanin-RI (2 µg/mL); MDR (2 µM); S. epidermidis (2 strains) (2 µM); VSE (3 strains) (2–4 µM); VRE (5 strains) (1–2 µM); Streptococcus (4 strains) (2–8 µM); C. jeikeium and L. monocytogenes (2–4 µM) |
| 39S |
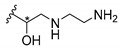
|
M. smegmatis (>19.3 µg/mL); M. bovis (>19.3 µg/mL) |
| 40S |
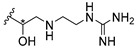
|
M. smegmatis (>21.8 µg/mL); M. bovis (>21.8 µg/mL) |
| 41S |
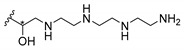
|
M. smegmatis (>24.5 µg/mL); M. bovis (>24.5 µg/mL) |
| 42S |
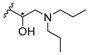
|
M. smegmatis (>21.8 µg/mL); M. bovis (>4.6 µg/mL) |
| 43S |
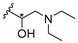
|
M. smegmatis (>4.3 µg/mL); M. bovis (>4.3 µg/mL) |
| 44S |
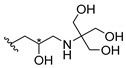
|
M. smegmatis (>19.9 µg/mL); M. bovis (>22.9 µg/mL) |
MIC: Minimum inhibitory concentration; MRSA: Methicillin-resistant S. aureus; MSSA: Methicillin-sensitive S. aureus; EMRSA: Epidemic methicillin-resistant S. aureus; MDR: Multidrug-resistant bacteria; VRE: Vancomycin-resistant E.; VSE: Vancomycin susceptible E.; * Stereogenic center.
