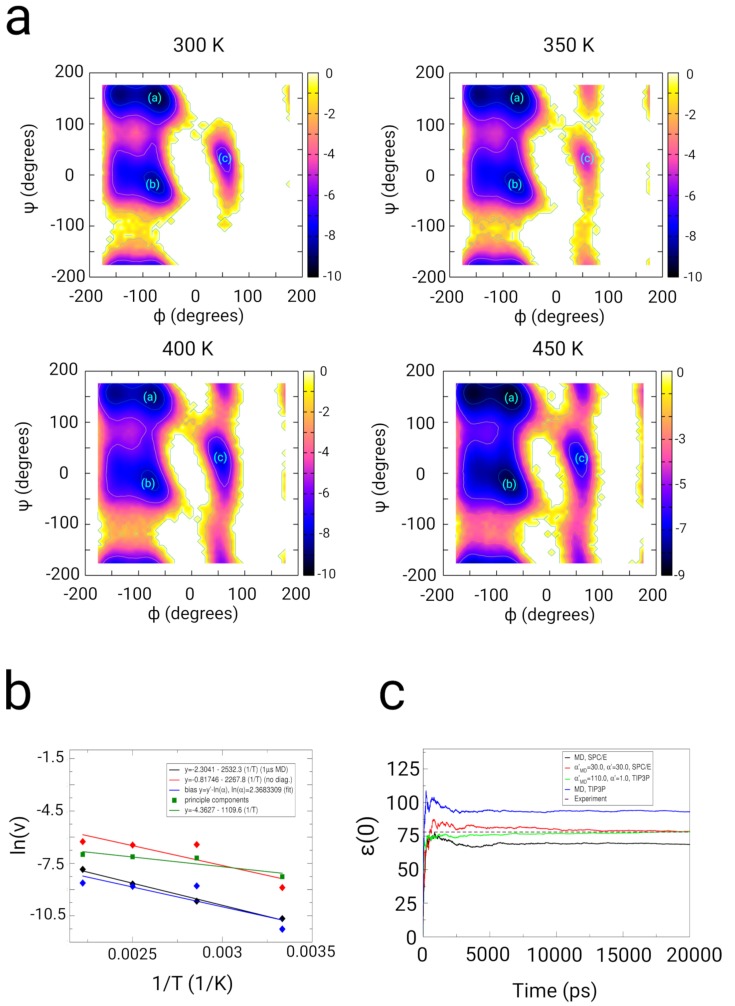
Figure 2.
Results from simulations of dialanine peptide in SPC/E water used for the validation of the sampling along multiple biasing increments (, adaptive bias MD) and (, path-sampling) to accelerate the sampling, which results in a biased action integral and a modification of the un-biased Hamiltonian , which results in a hybrid Hamiltonian . (a) Free energy landscapes as function of backbone dihedral angles and from simulations at the temperatures 300 K, 350 K, 400 K, and 450 K using multipe path sampling in combination with optimization techniques (using principal components of the biasing Hamiltonian ), a number of biases, , = 0.5 ps, and = 0.1 ps. Energy values on the color bar are in units of . (b) Comparison of the logarithm of the transition frequency of the dihedral angle as function of the inverse temperature (300–450 K) in the biased (red and green curve) and 1 s MD-trajectories (black curve) (blue curve, fit of the biased data to the MD-data for the determination of the linear scaling factor ln()). In this Kinetic analysis, we determined an acceleration factor equal to 10.68 by which the algorithm accelerates the sampling of dialanine peptide. (c) Static permittivities as function of MD-simulation time using different coupling and -parameters in the individual simulations of SPC/E and TIP3P water compared with conventional MD simulations.