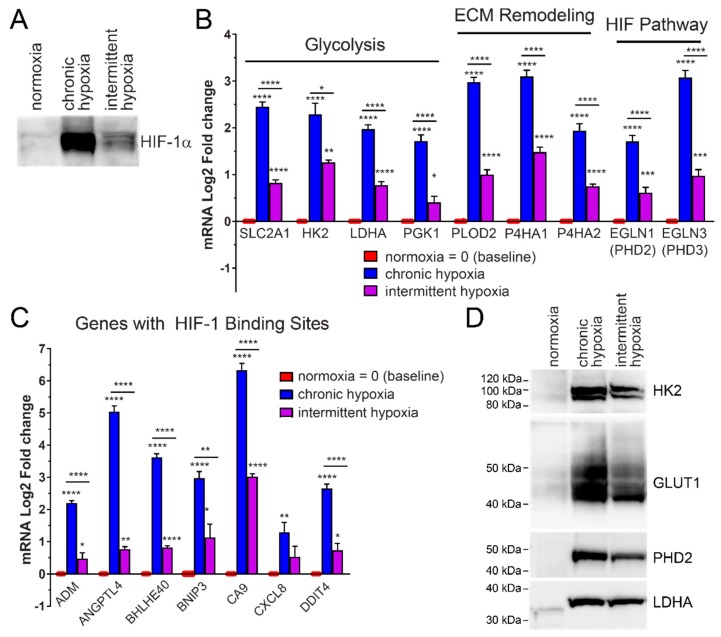
Figure 3.
HIF-1α protein increases in HCT116 cells exposed to rapid intermittent hypoxia. Increased HIF-1α increases HIF-1 transactivation, leading to increased expression of HIF-1 target genes at both the mRNA and protein level. (A) Rapid intermittent hypoxia increases HIF-1α protein after 6 h of exposure. (B) Rapid intermittent hypoxia increases the mRNA expression of genes involved in glycolysis, extracellular matrix remodeling and the HIF pathway after 18 h of exposure. (C) Additional genes with known hypoxia response elements (HRE) binding sites for HIF-1 were measured and all tested genes showed an increase in both chronic hypoxia and intermittent hypoxia after 18 h. All values were normalized to normoxic expression levels, which is equivalent to 0 on the Log2 scale. Results are the mean ± SEM of independent experiments run in duplicate (n ≥ 3). (D) The increase in mRNAs is also reflected in an increase in the protein levels of Glut1, HK2, LDHA and PHD2. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 and **** p < 0.0001.