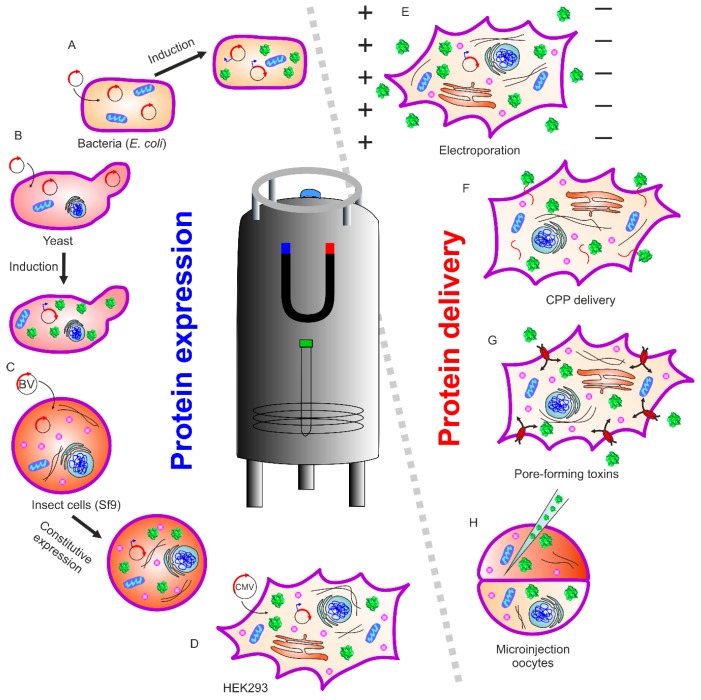
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of different known approaches in in-cell NMR. (Left) Endogenously expressed and isotopically labeled protein can be achieved by transferring the expression vector containing the gene of interest into (A) bacteria, (B) yeast, (C) insect cell lines, and (D) mammalian cells. (Right) An alternate way of in-cell NMR, where isotopically labeled protein is exogenously prepared followed by delivery into eukaryotic cells with different methods such as (E) electroporation, (F) attaching protein with cell-penetrating peptides (CPP), (G) protein transport via pore-forming toxins, and (H) microinjection-mediated delivery into Xenopus leavis oocytes.