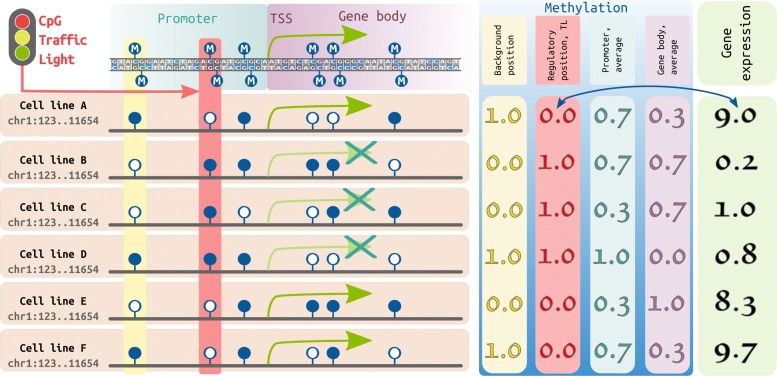
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of a CpG traffic light detection. Left panel. Suppose we analyze a particular genomic region (chr1:123..11654), which contains for simplicity one gene. For each CpG in this region and the gene we have methylation and expression vectors in 6 cell lines, respectively. CpG dinucleotides are represented by dark blue lollipops (filled: methylated CpG, empty: unmethylated CpG). First three CpGs are located within the promoter region, while the last three are located in the gene body. Gene expression or lack of it is represented by green arrows. Right panel. The yellow column shows methylation of a random CpG (used as a background), the methylation vector of this CpG demonstrates low correlation with the gene expression (the green box on the right, in RPKM). Correlation between the average promoter/gene body methylation (shown in the light blue and light purple columns, respectively) and the corresponding gene expression is also low. However, for the CpG TL (shown in the red box), the methylation significantly correlates with the gene expression