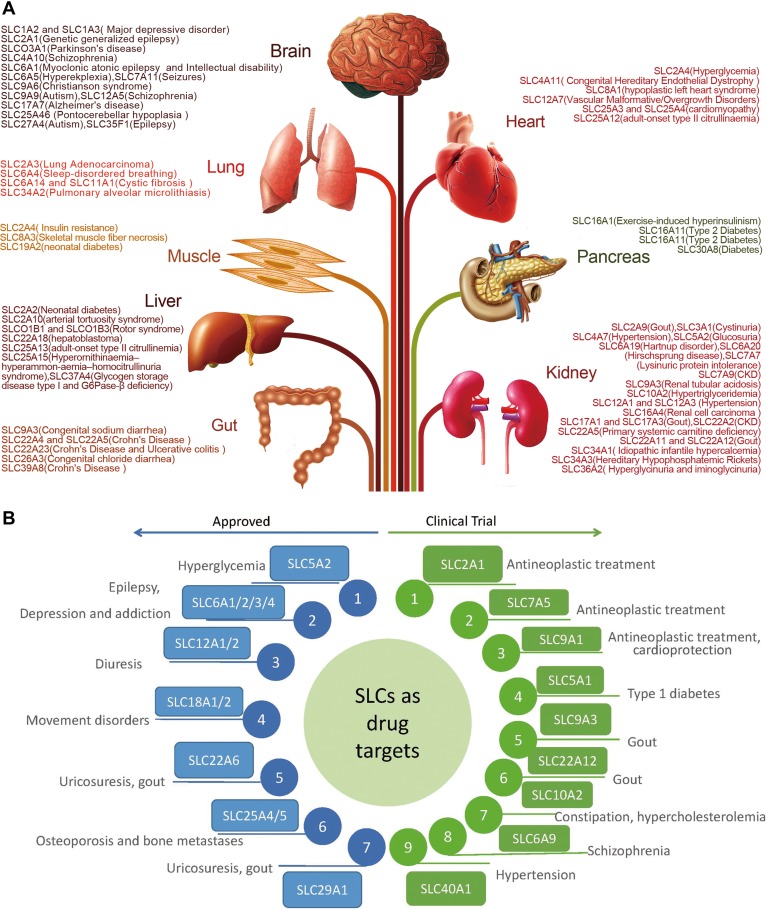
Figure 3.
(A) Tissues and diseases associated with SLCs. Major advances in understanding of the relationship between disease susceptibility and SLCs have been made. Accumulation of gene mutations and GWAS studies have demonstrated that SLCs play a crucial role in human diseases. SLCs are specifically expressed in different organs and involved in the pathogenesis of various human diseases. SLC members in the same family have been described that differ in the organ expression with different functions. The brain and kidney are two target organs for most high expression of SLCs-mediated diseases. Thus, SLCs are promising for neurologic and metabolic target. (B) SLC inhibitors for drug targets. The current SLC drug development is promising. Previous approved drugs were widely used for treatment of hyperglycemia, diuresis, movement disorders, uricosuresis, gout, and so on. Newly testing SLC drugs have the potential to exert antineoplastic effects, ameliorate Type 1 diabetes, resist constipation, protect from hypertension and schizophrenia. Data were cited from Rask-Andersen et al. (2013) and Cesar-Razquin et al. (2015).