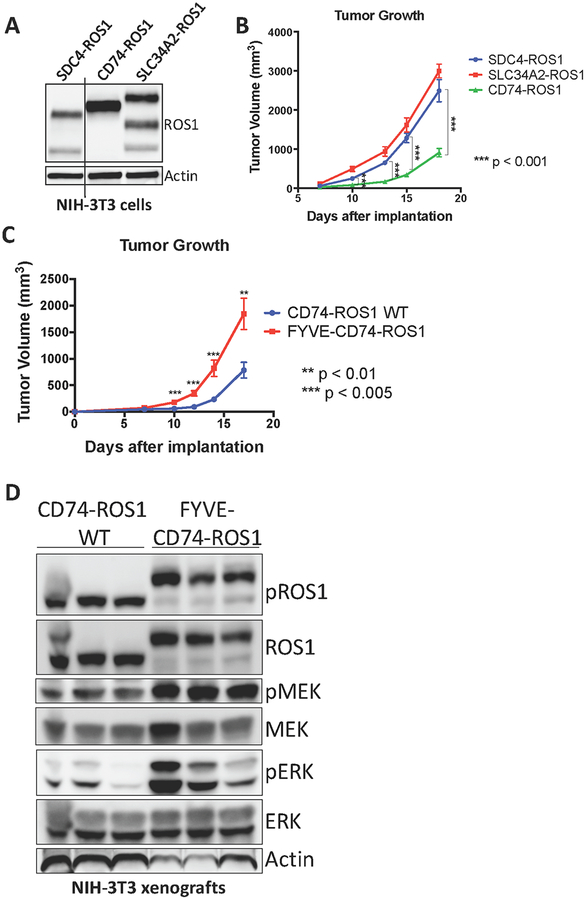
Figure 5. MAPK pathway activation in ROS1 fusion oncoprotein-driven cancer models is linked to increased tumorigenic properties in vivo.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of ROS1 fusion oncoprotein expression in isogenic NIH-3T3 cells. (B) Tumor growth rates of tumor xenografts of 1×106 NIH-3T3 ROS1 fusion oncoprotein-expressing cells described in (A) implanted into the flanks of immunocompromised mice. (C) Tumor growth rates of tumor xenografts of 5×105 cells NIH-3T3 cells expressing CD74-ROS1 WT or FYVE-tagged CD74-ROS1. (D) Immunoblot analysis of NIH-3T3 tumor xenograft explants expressing wild-type (WT) or FYVE-tagged CD74-ROS1. Each lane represents an individual tumor. Data in (B-C) are shown as the mean of 6 tumors +/− s.e.m.