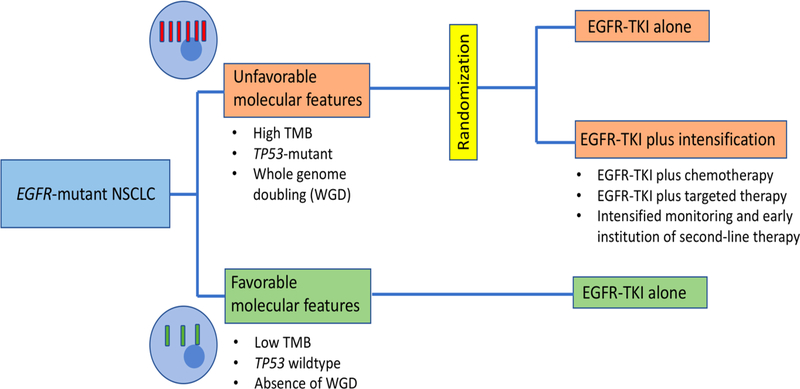
Figure 1: Schema for the investigation of intensified therapy in EGFR-mutant lung cancer harboring poor prognosis genomic biomarkers.
Genomic biomarkers are not routinely employed to guide therapy in EGFR-mutant NSCLC. Yet there could be a clinical role for such biomarkers in differentiating patients who do well with standard single-agent TKI from those who might benefit from studies of intensified therapy Prospective clinical trials which investigate intensified therapy (such as TKI-based combinations) in cases with unfavorable molecular features could help establish the clinical utility of such biomarkers.