Figure 1. Jablonski diagram.
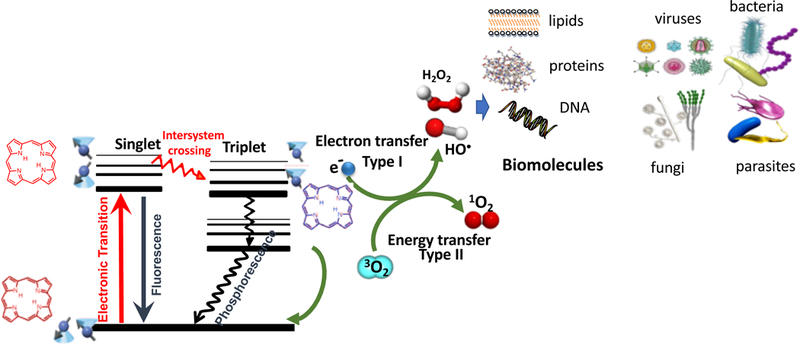
A ground-state PS absorbs a photon, transitions to the short-lived (nsec) excited singlet state that can undergo intersystem crossing to the long-lived (μsec) excited triplet state. The triplet PS can undergo energy transfer with ground state triplet oxygen (3O2) to form reactive singlet oxygen (1O2, Type 2) or else can undergo an electron transfer reaction to form HO•, superoxide and H2O2 (Type 1). These ROS (1O2 and HO•) can damage lipids, proteins and nucleic acids leading to destruction of all types of microbial cells, viruses and parasites.
