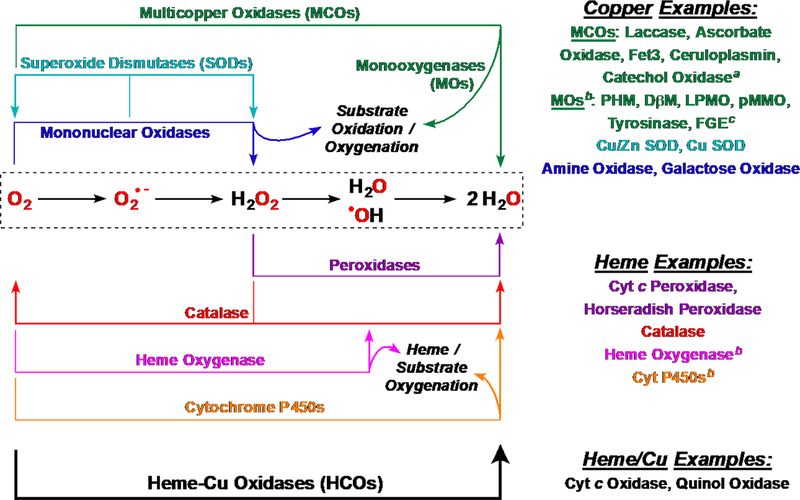
Figure 3.
Heme, copper, and heme/Cu enzymes involved in chemistry with dioxygen. aCatechol oxidase catalyzes four-electron reduction of dioxygen to two moles of water while oxidizing two moles of catechol substrate to two moles of quinone. bThe stoichiometry of monooxygenases (Cu-only and heme-only examples) reflects 2H+/2e− reduction of dioxygen to give one water molecule and incorporation of one O atom into a substrate (X-H → X–OH). cThe newly discovered formylglycine-generating enzyme (FGE) is a monooxygenase which is believed to utilize a mono-Cu site to oxidize cysteine to formylglycine and reduce O2 to form H2O and H2S (see section 3 for details).