Figure 6.
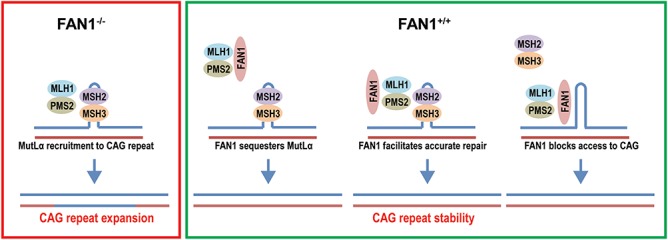
Mechanism of CAG repeat stabilization schematic showing a possible mechanism of FAN1 action. MutSβ (MSH2/MSH3) binds to abnormal structures formed by CAG repeat DNA, represented by a hairpin loop in the top strand. In the absence of FAN1 (purple box, FAN1−/−), MutLα (MLH1/PMS2) is recruited to the lesion by MutSβ. This leads to MMR activation, error-prone repair and CAG expansion. FAN1 expression (green box) may stability the CAG repeat by sequestering MutLα. This prevents its interaction with MutSβ thereby stopping MMR activation and CAG expansion. Alternatively, the association of FAN1 with the CAG repeat facilitates accurate repair, possibly by recruiting DDR components or FAN1 blocks access to the CAG repeat, preventing access to MMR components and CAG expansion.
