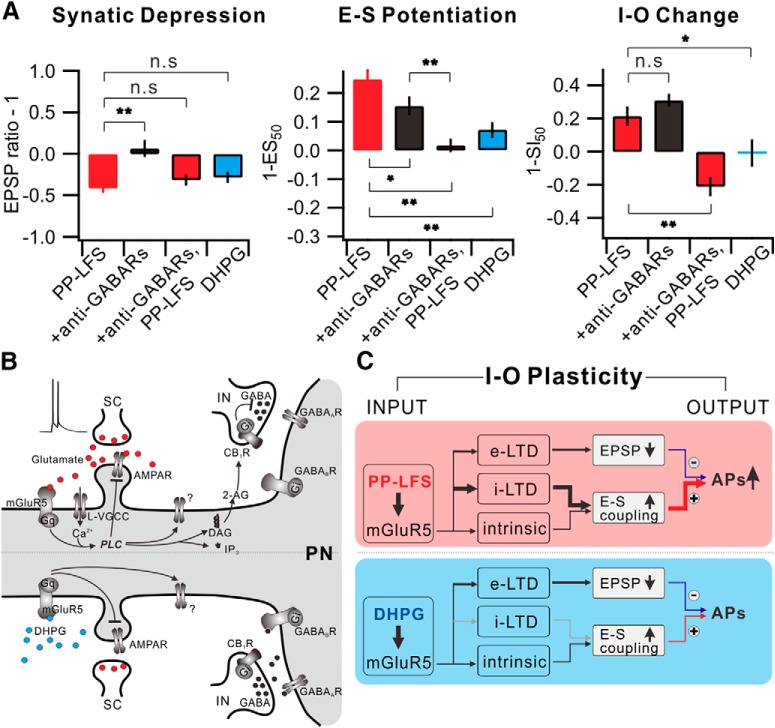
Figure 9.
Understanding I-O plasticity during e-LTD by integration of synaptic plasticity and E-S potentiation. A, Summarized data of changes in synaptic weight (left), E-S coupling (middle), and I-O change (right) in each condition. B, mGluR5-dependent downstream signaling mechanism induced by synaptic stimulation (top) or DHPG application (bottom) in CA1 pyramidal neuron. Gq, Gq protein; L-VGCC, L-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channel; AMPAR, AMPA receptor; IP3, inositol trisphosphate; IN, interneuron; PN, pyramidal neuron. C, Schematic diagram of I-O plasticity. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01. n.s., Not significant (p > 0.05). Error bars indicate SEM.