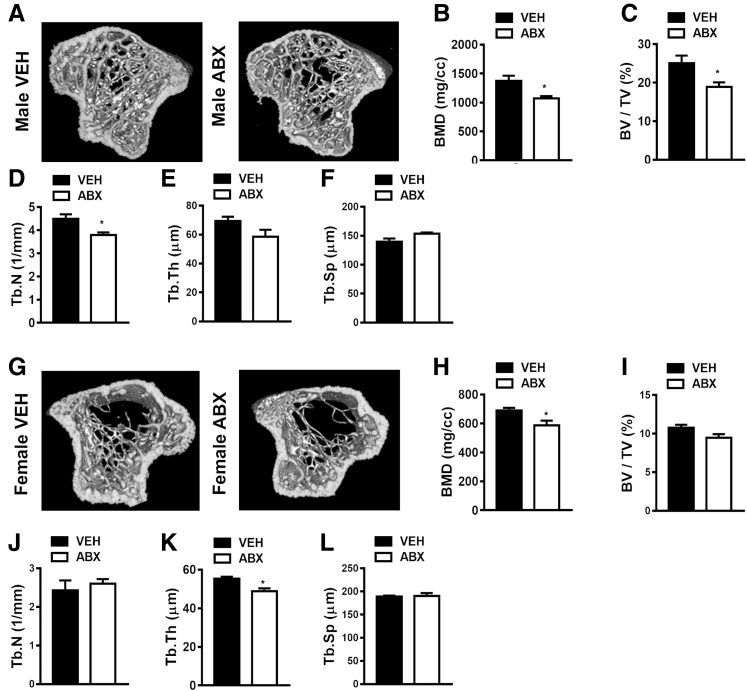
Figure 2.
Antibiotic (ABX) disruption of gut microbiota effects on bone mineral density (BMD) and trabecular bone morphology. Twelve-week–old male vehicle (VEH)– and ABX-treated mice and female VEH- and ABX-treated mice were euthanized; specimens were harvested for analysis. A–F: Micro–computed tomographic (μCT) analyses of the proximal tibiae trabecular bone in male VEH- and ABX-treated mice. A: Representative reconstructed cross-sectional images, extending 360 μm distally from where analysis was initiated, in male VEH- and ABX-treated mice. B: Male trabecular BMD. C: Male trabecular bone volume fraction (BV/TV). D: Male trabecular number (Tb.N). E: Male trabecular thickness (Tb.Th). F: Male trabecular separation (Tb.Sp). G–L: μCT analyses of the proximal tibiae trabecular bone in female VEH- and ABX-treated mice. G: Representative reconstructed cross-sectional images, extending 360 μm distally from where analysis was initiated, in female VEH- and ABX-treated mice. H: Female BMD. I: Female BV/TV. J: Female Tb.N. K: Female Tb.Th. L: Female Tb.Sp. Unpaired t-test was used. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 4 per group (A–L). ∗P < 0.05 versus vehicle. cc, cubic centimeters.