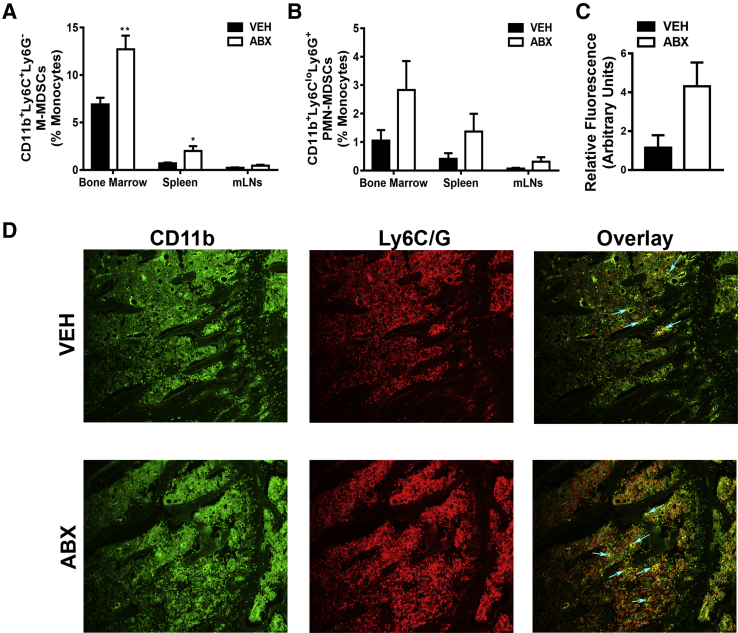
Figure 7.
Antibiotic (ABX) perturbation of gut microbiota influence on myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). Twelve-week–old male vehicle (VEH)– and ABX-treated mice were euthanized; specimens were harvested for analysis. A and B: Flow cytometric analysis of MDSC subset populations in bone marrow, spleen, and mesenteric lymph nodes (mLNs). Percentages of CD11b+Ly6C+Ly6G− (monocytic) MDSCs (M-MDSCs; A) and CD11b+Ly6CloLy6G+ (polymorphonuclear) MDSCs (PMN-MDSCs; B). Cell percentages are expressed relative to total gated monocyte cells. C and D: MDSC immunofluorescence analysis was performed on proximal tibia (secondary spongiosa) sections. C: Relative fluorescence of CD11b+Ly6C+Ly6G+ MDSCs. D: Representative MDSC immunofluorescence-labeled proximal tibia sections (green, CD11b-FITC; red, Ly6C/G-rhodamine); arrows indicate dual-labeled MDSCs. Unpaired t-test was used. Data are expressed as means ± SEM (A–C). n = 4 per group (A–D). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 versus vehicle. Original magnification, ×200 (D).