Figure 5.
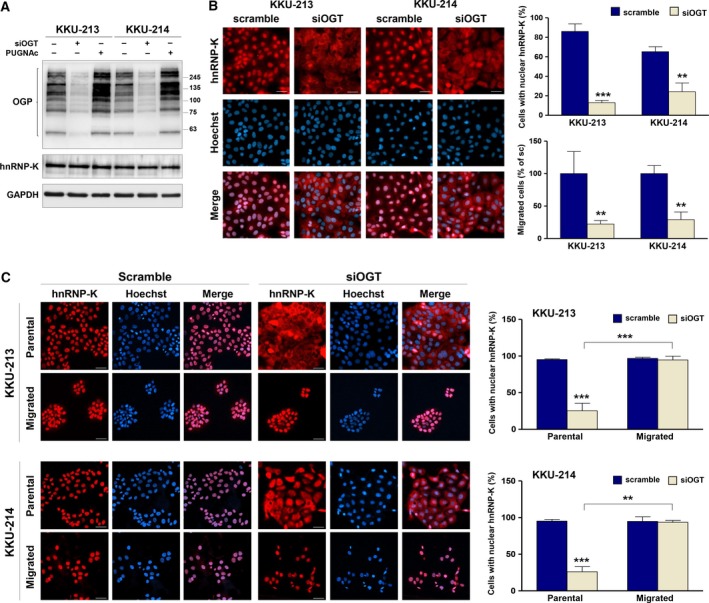
hnRNP‐K nuclear localization is regulated by O‐GlcNAcylation and correlated with migratory activity of CCA cells. (A) The expression of OGT was suppressed by siRNA for 24 h. Expression levels of OGP and hnRNP‐K in siOGT‐ and PUGNAc‐treated cells were compared with those of control cells using western blot analysis. (B) Localization of hnRNP‐K and nuclei was observed using immunocytofluorescent staining. hnRNP‐K was stained using PE (red), and cell nuclei were visualized using Hoechst 33342 (blue). Nuclear localization of hnRNP‐K is demonstrated by the purple nuclei in the merged images. The quantification of scramble siRNA‐ and siOGT‐treated cells with nuclear hnRNP‐K is shown in the upper panel graph. The migratory ability of cells treated with scramble siRNA and siOGT is shown in the lower panel graph. (C) The scramble siRNA‐ and siOGT‐treated cells were allowed to migrate to the lower chamber in a Transwell culture system for 48 h. Localization of hnRNP‐K was determined in the parental and migrated cells using immunocytofluorescent staining. Cells with nuclear hnRNP‐K were counted as shown in the graphs. The images are 200 × magnification and scale bars = 20 μm. Data are mean ± SD with **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 (Students’ t‐test).
