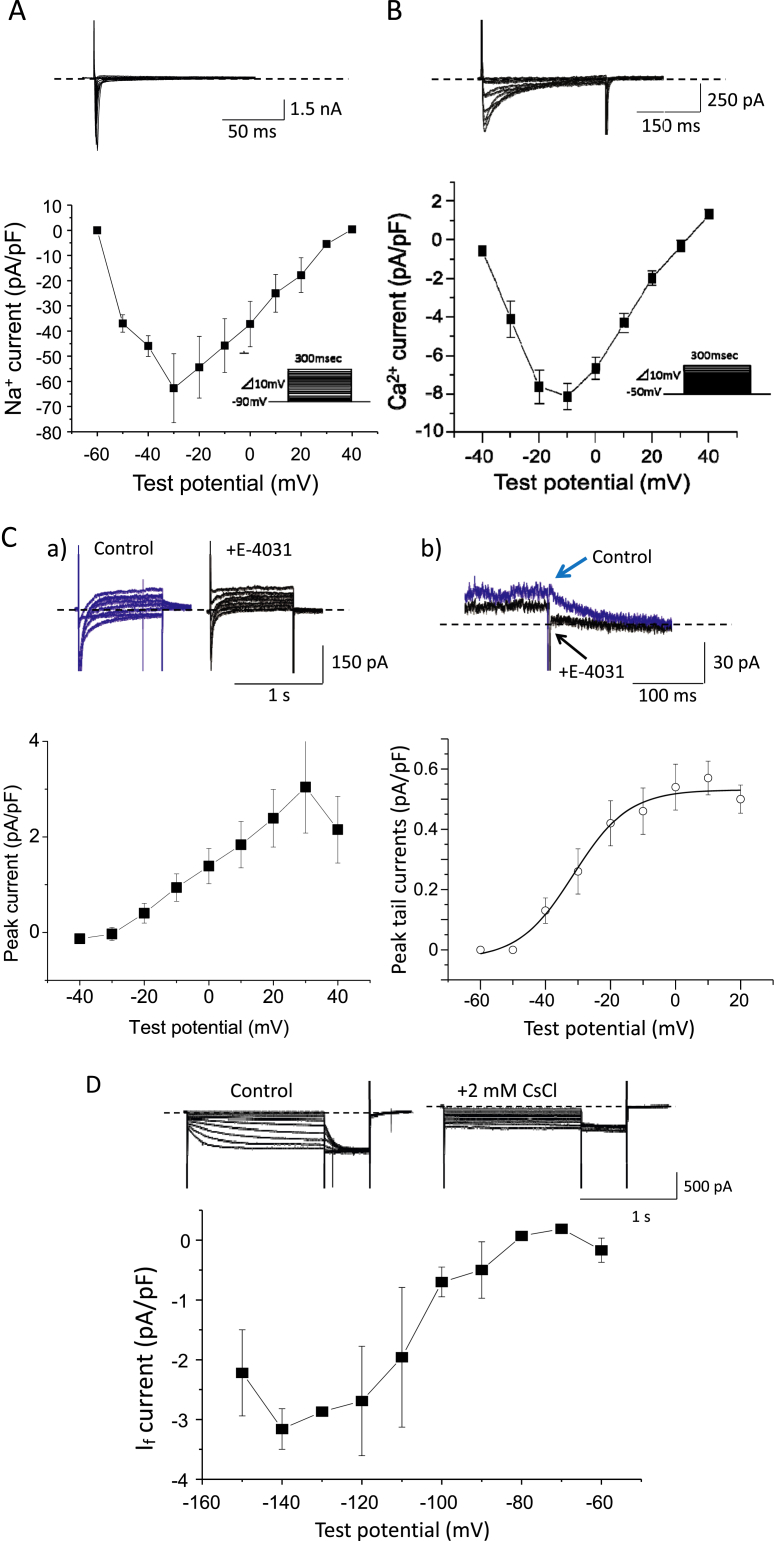
Fig. 2.
Characterization of sarcolemmal ionic currents in iCell cardiomyocytes. A: Representative original traces of the Na+ channel current (INa) elicited by 300-ms depolarization pulses from the HP of −90 mV (top) and current-voltage relationship for peak INa obtained from 10 cells (bottom). B: Representative original traces of the L-type Ca2+ channel current (ICaL) elicited by 300-ms depolarization pulses from the HP of −50 mV (top) and current-voltage relationship for peak ICaL obtained from 10 cells (bottom). C: Representative original traces of membrane currents elicited by 1-s depolarization pulses from the HP of −50 mV (a), as well as an expanded scale view of the tail currents during step repolarizations to the HP from 30 mV (b), in the absence (blue) and presence (black) of 1 μM E4031 are shown at the top. Note that 1 μM E4031 completely blocked the tail current. Current-voltage relationships for the E4031-sensitive current IKr determined at the end of depolarizing pulses (left) and peak tail currents during step repolarizations (right) are shown at the bottom (n = 10). D: Representative original traces of membrane currents evoked by 3-s hyperpolarizing pulses in the absence and presence of 2 mM CsCl (top) and current-voltage relationship for the Cs-sensitive If obtained from 10 cells (bottom).