Table 1.
Constituent compounds in A. africana extract and associated activities that enhance wound healing.
| S/No | Class of compound | Phytochemical compounds | Compound structure | Activities that enhances wound healing | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | Monoterpenes | carene |
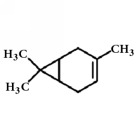
|
(i) Anti-inflammatory (ii) Antimicrobial |
[19–26] |
|
| |||||
| b | Phytocannabinoids | Caryophyllene |
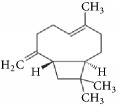
|
(i) Antimicrobial (ii) Anti-inflammatory |
[19, 27–35] |
|
| |||||
| c | Sesquiterpenes | Germacrene D |
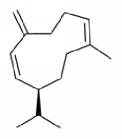
|
(i) Anti-inflammatory (ii) Anti-microbial and (iii) Anti-oxidant |
[36–44] |
|
| |||||
| d | Terpene | α-pinene |
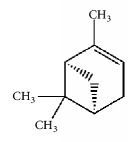
|
(i) Anti-microbial (ii) Anti-inflammatory (iii) Increases basic fibroblast growth factor (BFGF) (iv) Increases platelet derived growth factor |
[45–53] |
|
| |||||
| e | Acyclic diterpene alcohol | Phytol |
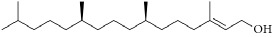
|
(i) Induces oxidative stress on microbial organisms (ii) Reduces interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α levels |
[4, 20, 54–60] |
|
| |||||
| f | Fatty acid | Linolenic acid |
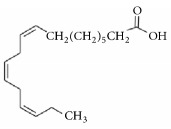
|
(i) Anti-microbial (ii) Down regulate inflammatory inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). |
[20, 61–63] |
