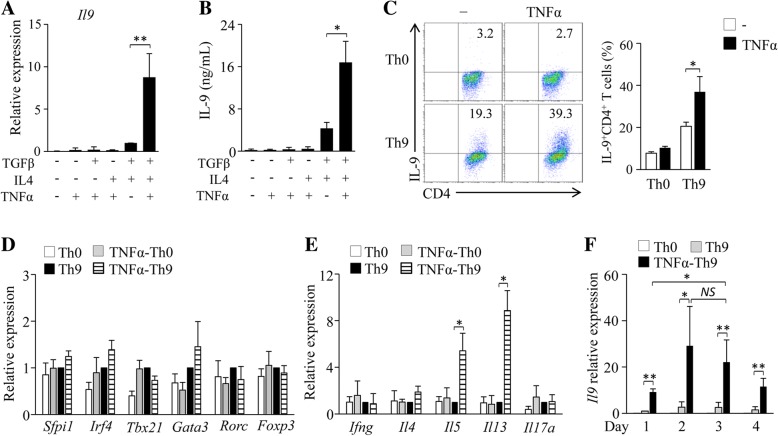
Fig. 1.
TNF-α drives Th9 cell differentiation in vitro. (a, b) Mouse naïve CD4+ T cells were cultured in the presence of anti-CD3/28 with the addition of TGF-β, IL-4, TNF-α or their combinations for 3 days. Cultures without the addition of any cytokines were used as controls. (a) qPCR analysis of Il9 gene expression in CD4+ T cells. Expression was normalized to Gapdh and set at 1 in cells treated with TGF-β plus IL-4 (Th9 cells). (b) ELISA assessment of IL-9 secretion in the cultures. (c-e) Naïve CD4+ T cells were cultured under Th9 polarizing conditions with or without addition of TNF-α for 3 days. Cell cultures without (Th0) addition of Th9-polarizing cytokines TGF-β and IL-4 were used as controls. (c) Flow cytometry analysis of IL-9-expressing CD4+ (IL-9+CD4+) T cells. Numbers in the dot plots represent the percentages of IL-9+CD4+ T cells. Right, summarized results of three independent experiments obtained as at left. (d, e) qPCR analysis of the indicated transcription factors (d) and cytokines (e). (f) Naïve CD4+ T cells were cultured under Th9 polarizing conditions in the presence or absence of TNF-α. Th0 cells were used as controls. Cells were collected at the indicated time points and qPCR analyzed the expression of Il9 in CD4+ T cells. Expression was normalized to Gapdh and set at 1 in Th9 cells collected on Day 1. Expression was normalized to Gapdh and set at 1 in Th9 cells. Data are representative of three (c) independent experiments or presented as mean ± SD of three (a-f) independent experiments. NS, non-significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01