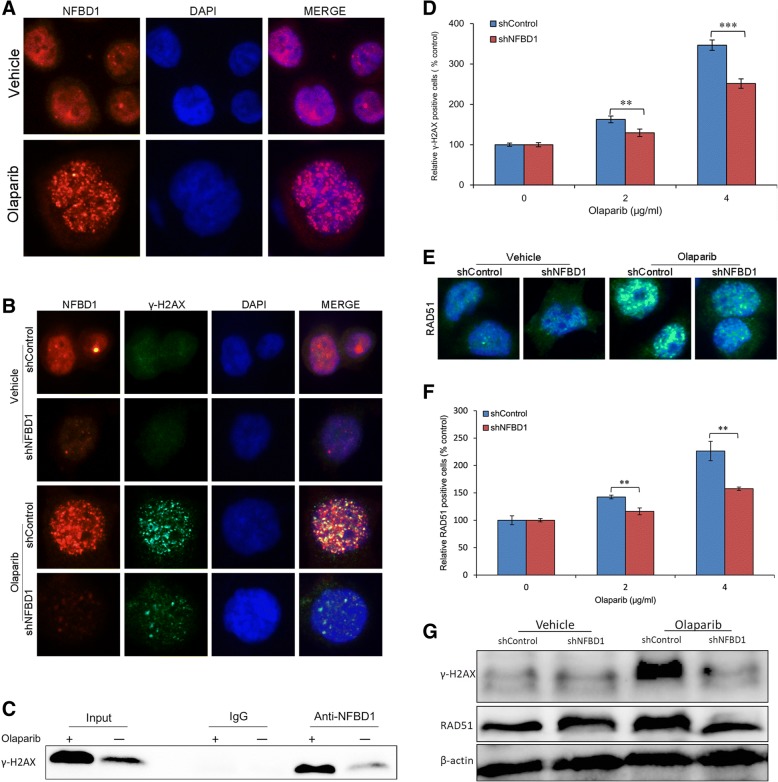
Fig. 5.
NFBD1 regulates olaparib-induced formation of γ-H2AX and Rad51 foci (a) Olaparib-induced NFBD1 foci formation. Inhibition of NFBD1 results in defective γ-H2AX foci formation after olaparib exposure, cells were exposed to olaparib for 24 h, and the γ-H2AX foci formation was detected by immunofluorescence (b) and the γ-H2AX positive cells were determined by FCM (d). (c) Association of NFBD1 with γ-H2AX. Coimmunoprecipitation was done with the antibody indicated or a non-specific, species-matched IgG control. Silencing NFBD1 inhibits RAD51 foci formation, and the RAD51 foci formation was determined by immunofluorescence (e) and the RAD51 positive cells was detected by FCM (f). (g) Cells were untreated or 4 μg/ml olaparib for 24 h, and subjected to western blotting analysis with indicated antibodies. Representative blots were shown with β-actin as loading control. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001