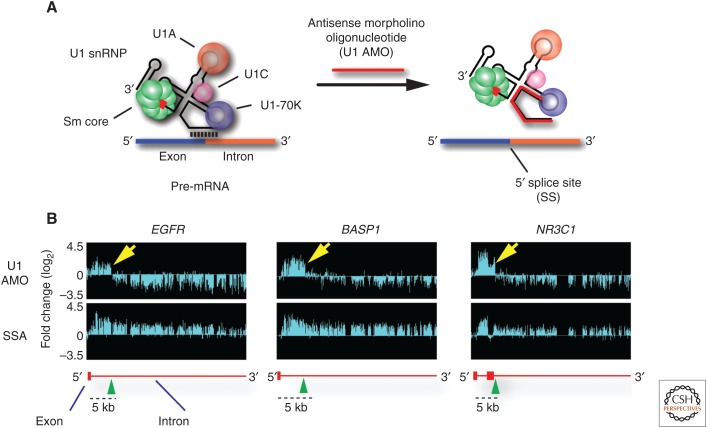
Figure 1.
Genomic tiling arrays detect, in U1 antisense morpholino oligonucleotide (AMO) transfected cells, transcripts extending from the transcription start site (TSS) of the genes EGFR, BASP1, and NR3C1 into the first part of the intron in which they abruptly end. (A) AMO (25-mer) to U1 snRNA’s 5′-end (U1 AMO) interferes with U1 snRNP (U1) base-pairing with 5′ splice sites, necessary for splicing of introns, and with other sequences on nascent transcripts. (B) Transcriptome profiling with genomic tiling arrays show the fold change in RNA signals compared with control. The top panel shows that, in addition to inhibiting splicing, U1 AMO also induces premature 3′-end cleavage and polyadenylation (PCPA) as RNA reads downstream from these end points are strongly decreased. In contrast (bottom panels), splicing inhibition with spliceostatin A (SSA) shows RNA reads increasing over the full length of introns, as expected for unspliced pre-mRNAs. Schematic gene structures (based on RefSeq, hg19) are depicted in red, with horizontal lines indicating introns and boxes indicating exons.