Figure 1.
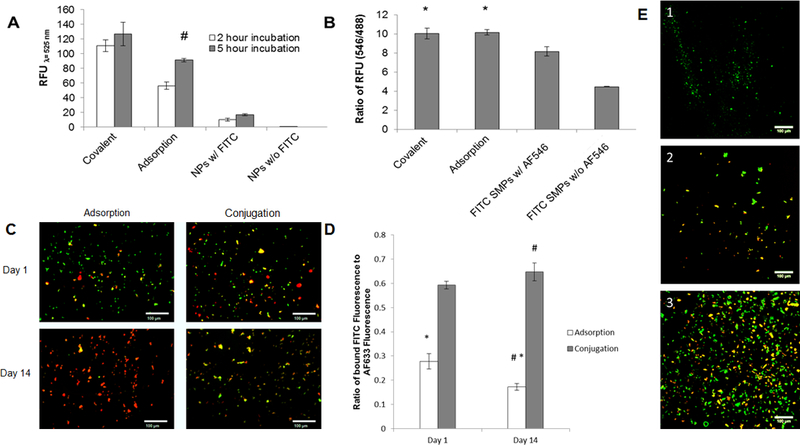
UV spectroscopy analysis of PLGA SMPs conjugated with cathepsin K antibody. Panel 1A shows effect of incubation time on conjugation of the antibody to SMPs. The cathepsin K antibody was detected with a fluorescein-tagged secondary Ab. A higher fluorescence intensity (RFU) indicates more effective antibody conjugation. Panel 1B compares relative abundance of conjugated antibodies on the SMPs. Cathepsin K antibodies were conjugated onto fluorescein-loaded SMPs over 5 hours, and were detected with secondary antibodies tagged with AF546. Values shown indicate mean ± SD of RFUs (Panel A) or of ratios of RFUs due to the fluorescein and AF546; n = 3 per case; # denotes significance of differences versus 2 h of incubation, deemed for p < 0.05; * denotes significance of differences versus control FITC SMPs treated with the AF-546-tagged secondary antibody, deemed for p< 0.05. Panels 1C, 1D show results of fluorescence microscopy analysis of cathepsin K surface modification to AF633-loaded SMPs (red). A fluorescein antibody (green) was added to visualize the cathepsin K modification. Panel C shows representative images for the adsorption and conjugation methods at day 1 and day 14. The green fluorescence demonstrates successful cathepsin K conjugation to the SMP surface. At day 14, green fluorescence associated with SMPs modified using Ab-adsorption was much lower compared to SMPs chemically conjugated with the Abs. Panel 1D shows the ratio of FITC intensity to AF633 intensity (mean ± SE; adsorption n=132, n=130 and conjugation n=154, n=207). The conjugation method bound more cathepsin K to the SMP surface for a longer period of time. # denotes significance of differences between adsorption and conjugation on day 14 deemed for p<0.05. * denotes significance of differences between day 1 and day 14 for the adsorption method deemed for p<0.05. In panel 1E, confocal micrographs compare cathepsin K antibody bound to SMPs via adsorption and covalent conjugation methods (see quantitative data in panel 1B). Conjugation was performed over 5 hours. Fluorescein (green) was encapsulated within the SMPs and the cathepsin K antibody was detected with an AF546-tagged secondary antibody (red). Panel 1E1 shows lack of red auto-fluorescence from cathepsin K antibody-conjugated SMPs not treated with the AF546-tagged secondary antibody. Panels E2 and E3 show that cathepsin K antibody was successfully conjugated to the SMPs using the adsorption- and covalent binding methods respectively. Scale bar: 100 μm (panel C), 100 μm (panel E).
