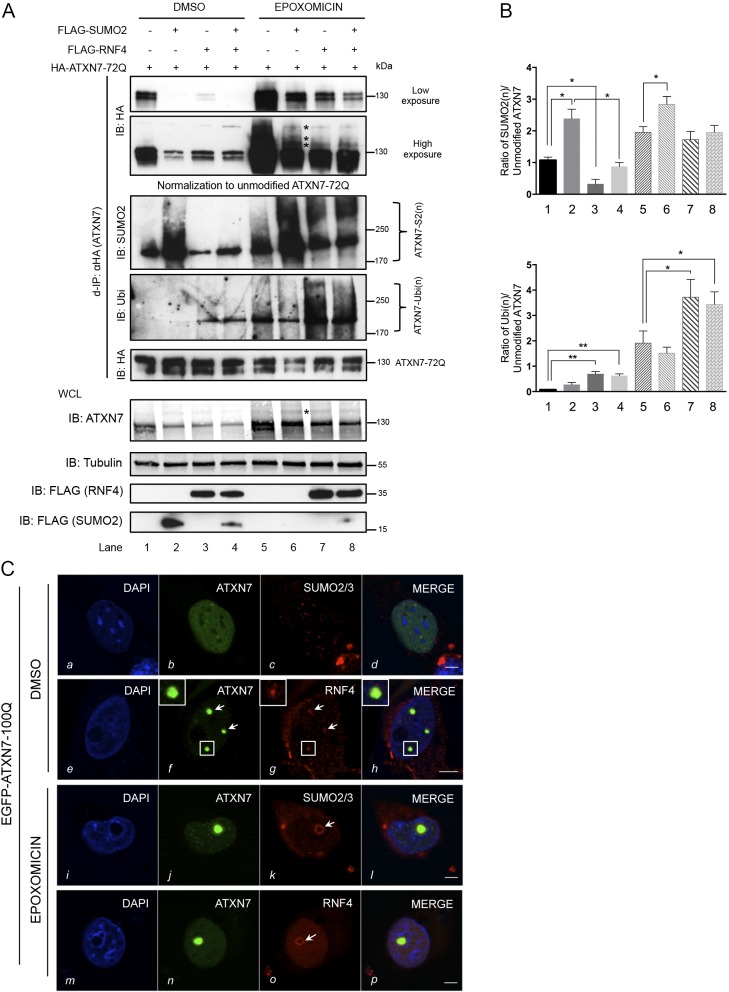
Fig. 4.
Proteasome inhibition abolishes mutant ATXN7 degradation via RNF4. (A) HEK293 cells overexpressing ATXN7-72Q, SUMO2 and RNF4 were treated with DMSO (control) or epoxomicin (1 µM for 16 h). Denaturing immunoprecipitation (d-IP) samples with similar levels of unmodified ATXN7-72Q were analyzed, as normalization is required for a comparison of modified ATXN7 levels. d-IP products, before normalization (top panel, low and high exposures; asterisks indicate poly-SUMO2 modified HA-ATXN7-72Q), and input in whole-cell lysate (WCL; bottom panel; asterisk indicates SUMO2-modified ATXN7) are shown. d-IP products after normalization are shown in the middle panel (IB: SUMO2, IB: Ubi, IB: HA). Co-expression of RNF4 and SUMO2 decreased SUMO2-modified ATXN7. Epoxomicin treatment led to SUMO2- (IB: SUMO2) and ubiquitin- (IB: Ubi) modified ATXN7 accumulation. RNF4 promoted the ubiquitination of modified ATXN7. (B) Top: quantification of the ratio of polySUMOylated ATXN7-S2(n)/unmodified HA-ATXN7-72Q in DMSO (lanes 1-4) and epoxomicin conditions (lanes 5-8). Bottom: quantification of the ratio of polyubiquitinated ATXN7-Ubi(n)/unmodified HA-ATXN7-72Q. Data are mean±s.d. (n=3). Statistical analysis was performed using Student's t-test: *P<0.05, **P<0.01. (C) Colocalization of expressed EGFP-mutant ATXN7 with endogenous SUMO2/3 and endogenous RNF4 in HeLa cells in control (DMSO, a-h) or epoxomicin (i-p) conditions. Endogenous RNF4 was detected in a subset of ATXN7-positive inclusions in the control condition (f, g, see arrows and higher magnification images), but following epoxomicin treatment became enriched around one large EGFP-ATXN7-100Q inclusion (o, arrow). SUMO2/3 shows a similar enrichment around an ATXN7 inclusion when proteasomal degradation is blocked (k; the arrow points to endogenous SUMO2/3 surrounding one large EGFP-ATXN7-100Q inclusion in epoxomicin-treated cells). Representative confocal images are shown. Scale bars: 5 μm.