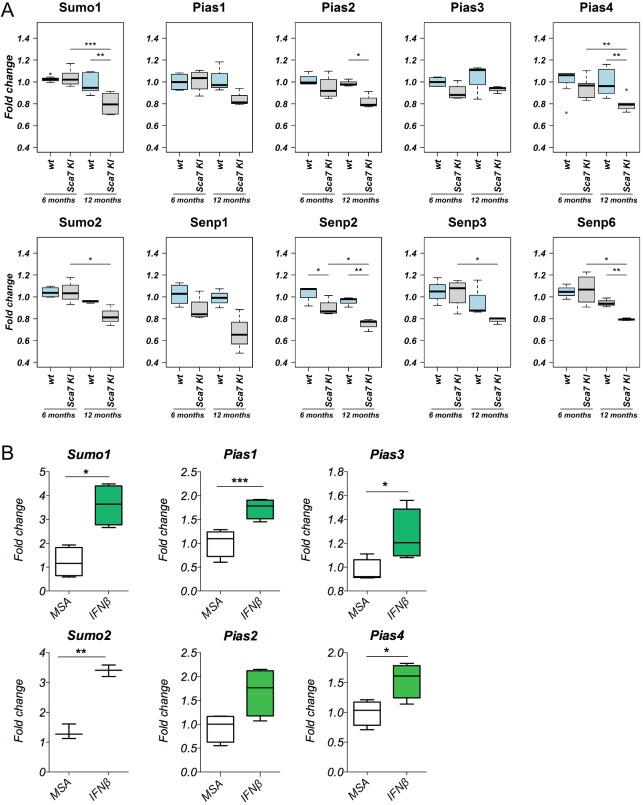
Fig. 6.
Expression of SUMO pathway-related genes in two SCA7 knock-in mice models. (A) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of SUMO pathway enzymes in cerebella from 6- and 12-month-old Atxn7100Q/5Q mice and wild-type littermates. SUMO enzymes were differentially expressed in 6-month-old Atxn7100Q/5Q versus wild-type mice; a statistically significant decrease was observed only for Senp2 (P=0.047). At 12 months, a statistically significant decrease in Sumo1 (P=0.0048), Pias2 (P=0.028), Pias4 (P=0.024), Senp2 (P=0.0079) and Senp6 (P=0.0021) was observed. Comparison between 6-month-old and 12-month-old Atxn7100Q/5Q mice confirmed the significant decrease in Sumo1 (P=0.0002), Sumo2 (P=0.035), Pias4 (P=0.007), Senp2 (P=0.038), Senp3 (P=0.027) and Senp6 (P=0.023) mRNA expression. Samples were analyzed in triplicate and normalized to mouse Rplp0 and B2m. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR of SUMO mRNAs from cerebella of 12 week-old SCA7266Q/5Q knock-in mice, injected intraperitoneally with either mouse IFN-beta or MSA (control). SUMO enzymes were significantly increased in IFN-beta-treated mice versus MSA controls: Sumo1 (P=0.0158), Sumo2 (P=0.0097), Pias1 (P=0.0009), Pias3 (P=0.0183), Pias4 (P=0.0133). Samples were analyzed in triplicate and normalized to mouse Rplp0 ribosomal gene. One-way ANOVA was applied for statistical analysis. Data are mean±s.d. (n=5 in each group). *P<0.05; **P<0.005; ***P<0.0005.