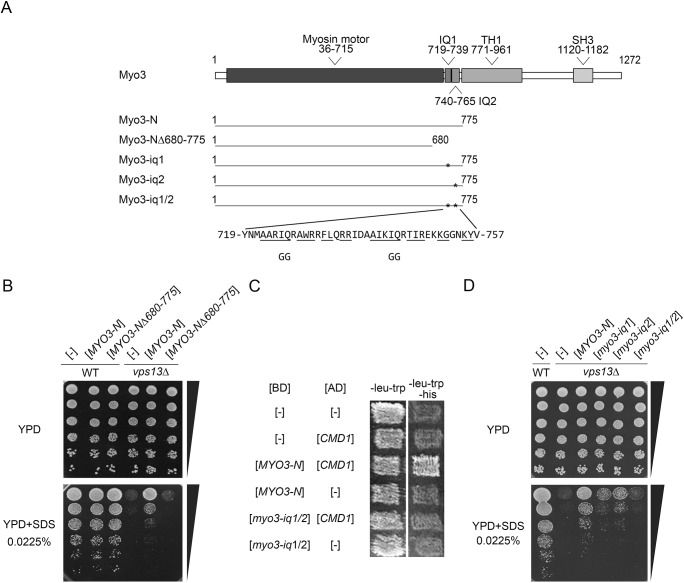
Fig. 2.
The MYO3-N fragment encoding the motor domain and calmodulin-binding motifs from Myo3 suppresses hypersensitivity of vps13Δ to SDS. (A) Schematic representation of Myo3 domain structure and Myo3 variants studied. Myo3 domains and motifs are based on the Uniprot database (http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P36006, 02.08.2018). *, position of mutations introduced in vitro. Amino acids conforming to the consensus of the calmodulin-binding motif as defined in the SMART database (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de, 02.08.2018). IQ motifs are underlined and amino acid substitutions are shown. (B) MYO3-N suppresses vps13Δ but MYO3-NΔ680-775 does not. (C) Myo3-N interacts with calmodulin in the two-hybrid system and mutations in IQ motifs abolish this interaction. BD, DNA-binding domian; AD, activating domain. (D) IQ motifs of Myo3 are required for suppression of vps13Δ.