Fig. 1.
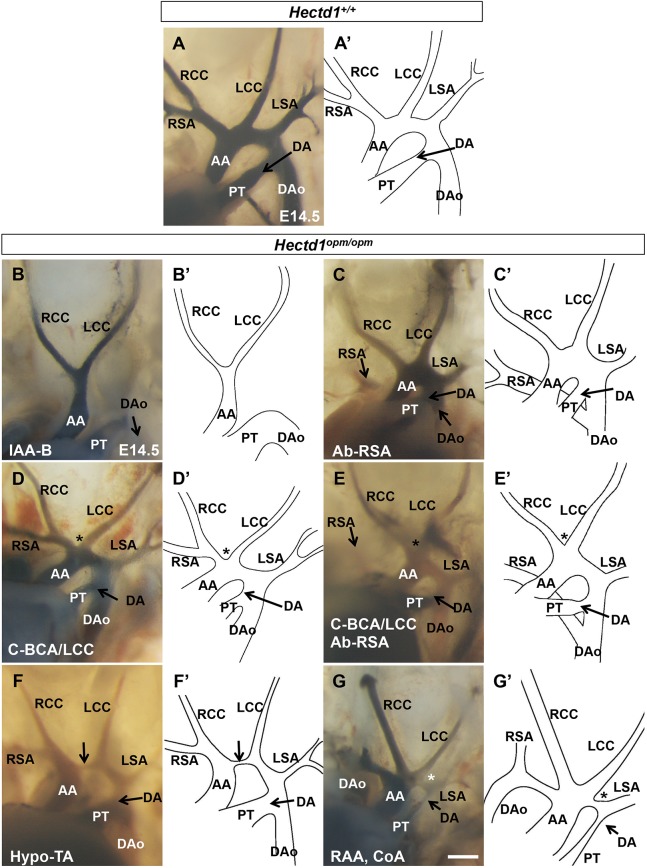
Abnormalities of the aortic arch in Hectd1opm/opm mutant embryos. (A) Intracardiac ink injections of E14.5 wild-type embryos (n=10), highlighting the normal mature artery architecture. A′-G′ show tracings of ink-labeled arteries in A-G. (B-G) 90% of the Hectd1opm/opm mutants analyzed demonstrated aortic arch abnormalities (n=9/10; Table 1) that included interrupted aortic arch type B (n=5; IAA-B) (B), aberrant origin of the right subclavian artery (n=4; Ab-RSA) (C), common origin of the brachiocephalic and left common carotid arteries (n=3; C-BCA/LCC, black asterisks) (D) or both C-BCA/LCC and Ab-RSA (n=2) (E). Other variants such as hypoplasia of the transverse arch (n=2; Hypo-TA, arrow) (F) and right-sided aortic arch with coarctation of the aorta (n=2; RAA, CoA, white asterisk) (G) were also observed. AA, ascending aorta; DA, ductus arteriosus; DAo, descending aorta; LCC, left common carotid; LSA, left subclavian artery; PT, pulmonary trunk; RCC, right common carotid; RSA, right subclavian artery. Scale bar: 250 µm.