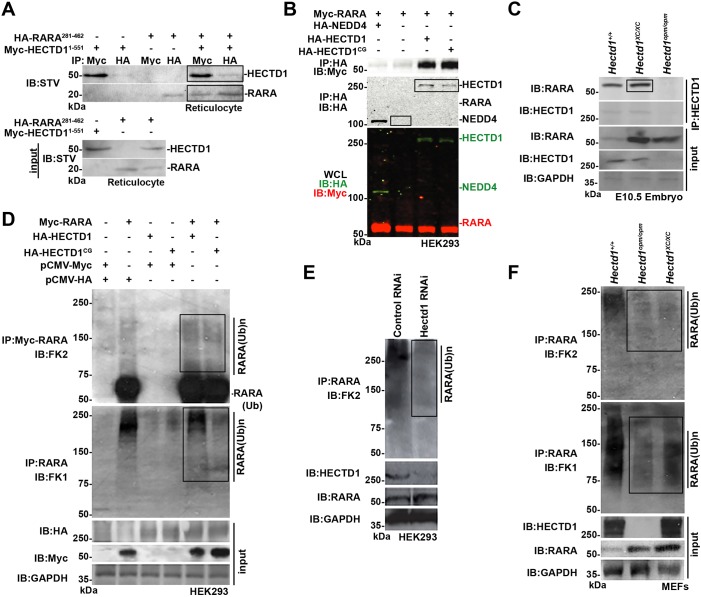
Fig. 3.
HECTD1 binds to RARA and influences its ubiquitination. (A) HA-RARA(281-462), binds to Myc-HECTD1(1-551) expressed in rabbit reticulocyte lysates. Proteins were immunoprecipitated (IP) as indicated followed by immunoblotting (IB) with streptavidin (STV). (B) RARA binds to HA-HECTD1 and ligase-deficient HA-HECTD1C2579G (HA-HECTD11CG), but not to HA-NEDD4, another HECT domain-containing E3 ligase, in HEK293T cells. WCL, whole-cell lysate. (C) RARA binds HECTD1 in vivo in embryo lysates prepared from E10.5 wild-type and Hectd1XC/XC mutant embryos. The epitope recognized by the HECTD1 antibody used for immunoprecipitation is not present in Hectd1opm/opm mutant embryos, thus the failure of HECTD1opm to pull down RARA serves as a negative control. (D) HECTD1 influences ubiquitination of RARA. HEK293T cells were transfected with Myc-RARA and either HA-HECTD1 or ligase-deficient HECTD1C2579G. RARA was immunoprecipitated followed by immunoblotting with the FK2 antibody to detect poly- and monoubiquitinated RARA, or FK1 antibody to detect polyubiquitinated RARA. FK2 immunostaining indicates a slight increase in ubiquitinated RARA levels with expression of either wild-type or ligase-defective HECTD1, whereas FK1 immunostaining shows reduced ubiquitinated RARA in HA-HECTD1C2579G transfected cells, consistent with the predicted dominant-negative activity of this construct. (E) Knockdown of HECTD1 by siRNA in HEK293T cells results in decreased ubiquitinated RARA. (F) MEFs derived from Hectd1opm/opm and Hectd1XC/XC mutant embryos demonstrate reduced ubiquitinated proteins in RARA immunoprecipitates and increased RARA levels in mutant compared with wild-type cells. Key positive signals are highlighted in boxes.