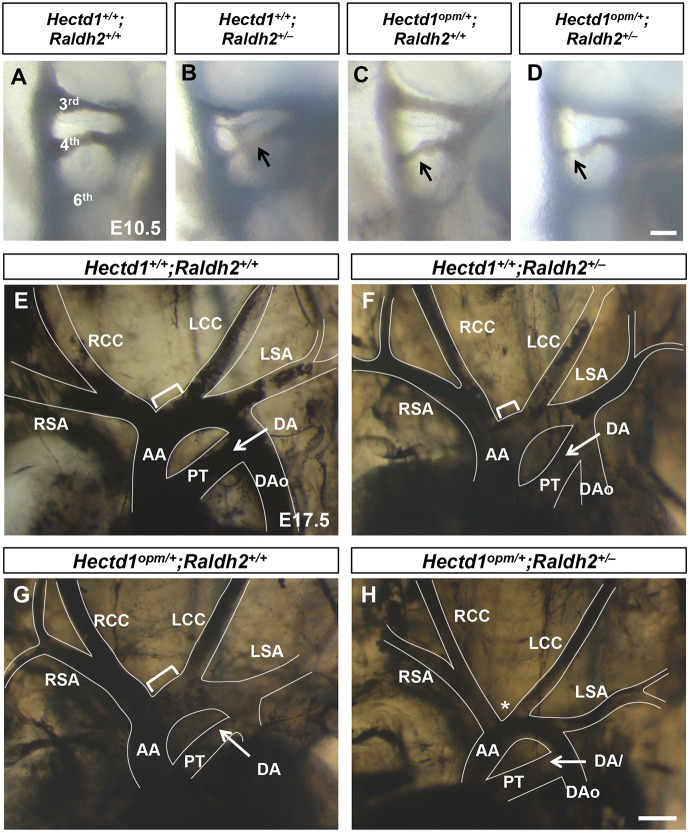
Fig. 5.
Reduced Raldh2 gene dosage results in PAA and aortic arch abnormalities in heterozygous Hectd1opm/+ mutant embryos. (A-H) Intracardiac ink injections of E10.5 (32- to 36-somite; A-D) and E17.5 (E-H) embryos to visualize the PAAs and aortic arch organization. (A-D) Right-sided views of E10.5 wild-type (Hectd1+/+;Raldh2+/+; A), Hectd1+/+;Raldh2+/− (B), Hectd1+/opm;Raldh2+/+ (C) and Hectd1+/+;Raldh2+/+ (D) embryos, showing the 3rd, 4th and 6th PAAs, with examples of hypoplastic 4th PAAs (arrows). Few wild-type (n=3/16, 19%), Hectd1+/+;Raldh2+/– (n=3/11, 27%) and Hectd1opm/+;Raldh2+/+ (5/12, 42%) embryos showed hypoplastic 4th PAAs (Table 3). On the other hand, the 4th PAA was hypoplastic in two-thirds of double heterozygous Hectd1opm/+;Raldh2+/– embryos (n=11/16, 69%, P<0.0001, compared with wild type by Chi2 test). (E-H) At E17.5, 70% (7/10) of Raldh2 heterozygotes (F) and 71% (5/7) Hectd1 heterozygotes demonstrate similar length of the transverse arch between the brachiocephalic and left common carotid arteries (brackets) compared with wild type (E). This segment is shortened in Hectd1opm/+;Raldh2+/– double heterozygotes (H, asterisk), resulting in a shortened transverse arch between the brachiocephalic and left common carotid arteries in over half of embryos examined (4/7, 57%; P<0.05, Chi2 test). Scale bars: 50 µm (D) and 250 µm (H). AA, ascending aorta; DA, ductus arteriosus; DAo, descending aorta; LCC, left common carotid; LSA, left subclavian artery; PT, pulmonary trunk; RCC, right common carotid; RSA, right subclavian artery.