Fig. 1.
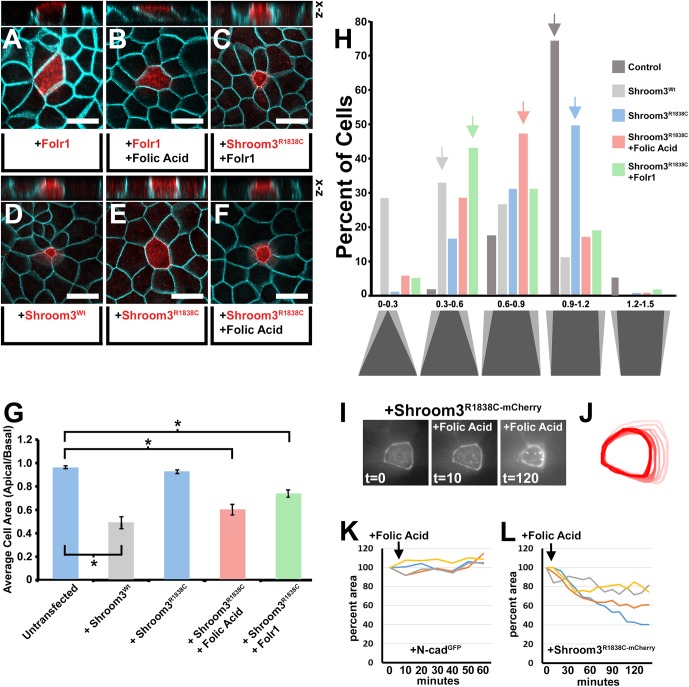
Exogenous folic acid and Folr1 rescues the function of a Rho-kinase binding mutation in Shroom3. (A–F) Apical views of MDCK cells transfected with the indicated expression vector, incubated with or without exogenous folic acid (100 µM) and immunofluorescently labeled with β-catenin (turquoise) and either Shroom3 or Folr1 antibodies (red). Above each panel is a virtual section through the transgenic cell in the x-z plane. Scale bar: 20 µm. (G) The mean apical basal area ratio (ABAR) was calculated from area measurements of apical and basal images of transgenic cells and depicted in the graph. Asterisks indicate data sets with significantly reduced ABAR ratios P<0.01. (H) The shapes depict the approximate shape range of cells with the indicated ABARs in increments of 0.3. The percentage of cells within specific ABAR increments are represented for the indicated experimental groups. Arrows mark the ABAR increment group with the greatest number of cells. Note that the experimental groups have distinct peak ABAR increment ranges indicating a shift in the population. (I) Time-lapse images of a Shroom3R1838C-mCherry tagged transgenic cell before and after the addition of folic acid (100 µm). (J) The apical outline of the transgenic cell in I was traced at each time point and superimposed to show the radial reduction of apical area. (K–L) The change in apical area was plotted with time following folic acid treatment of four representative transgenic cells expressing either N-cadherin-GFP or Shroom3R1838C-mCherry.