Fig. 6. mm-NFC dosimeters with separate, independent operation at IR to the UV wavelengths.
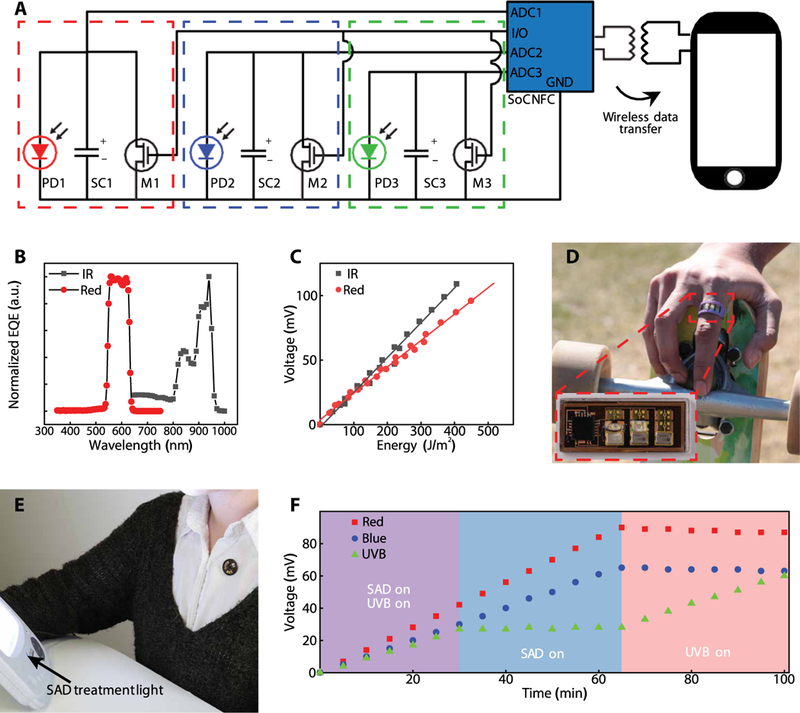
(A) Circuit diagram of the device and wireless communication to a smartphone. The configuration uses three separate ADCs on a single NFC chip, three SCs (SC1, SC2, and SC3), three MOSFETs (M1, M2, and M3), a single GPIO for reset and three separate photodetectors (PD1, PD2, and PD3). (B) EQE spectrum of broadband red and IR PDs (n = 1). (C) Voltage measurements from an mm-NFC sensor (n = 1) operating in the IR/red as a function of exposed energy at each corresponding wavelength range. (D) Image of an mm-NFC dosimeter with operation in the UVA/UVB/IR configured as a ring. Inset shows higher magnification. (E) Image of an mm-NFC dosimeter with operation in the UVB/red/blue as a shirt-worn badge in front of a white light phototherapy lamp. (F) Results of cumulative dosimetry using a UVB/red/ blue mm-NFC device (n = 1) during exposure with different light sources, illustrating stable, separate operation across corresponding regions of the spectrum.
