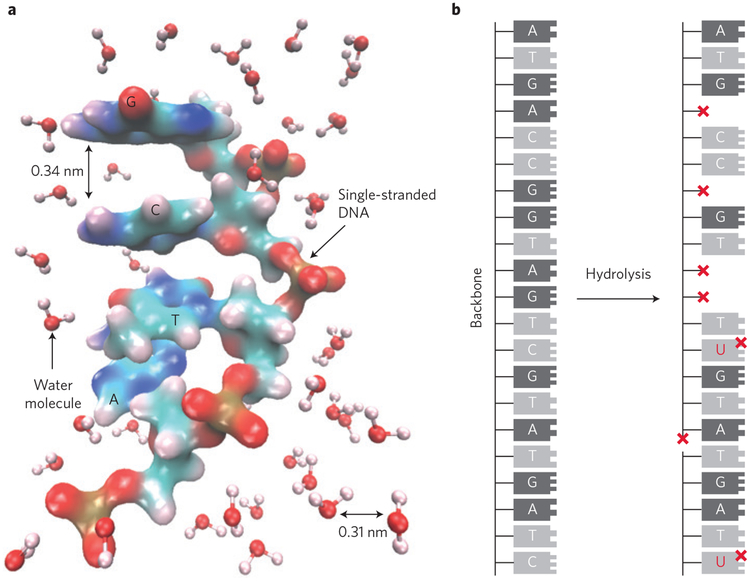
Figure 2 |.
Mechanism of NAM information degradation by hydrolysis. a, Simulated model of a single-stranded DNA molecule in an aqueous environment. b, Illustrated mechanisms of depurination (red crosses in place of DNA bases), backbone cleavage (red cross in the DNA backbone), and point mutations resulting from deoxycytidine deamination (red crosses next to DNA bases).