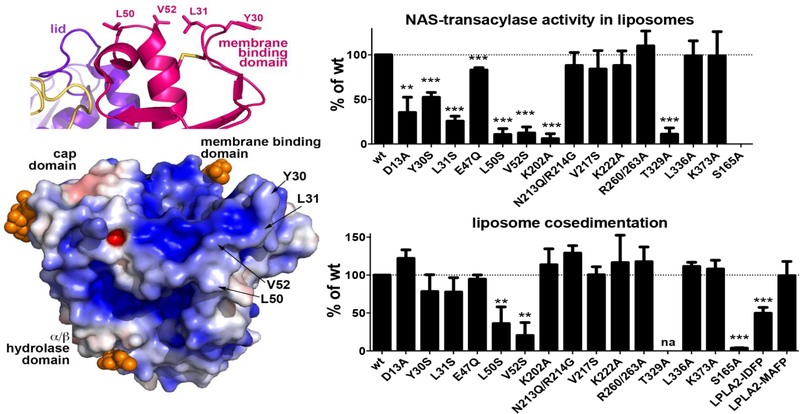
Figure 4.
Left upper panel. Surface hydrophobic residues Y30, L31, L50 and V52 constitute part of the PLA2G15 membrane binding surface. Left lower panel. Surface electrostatic potential of PLA2G15, calculated at pH 5. Mutation of hydrophobic residues to hydrophilic serines reduces PLA2G15 activity on liposomes (right upper panel) and liposome binding (right lower panel). PLA2G15 ability to form an acyl-intermediate is crucial for stable membrane binding. Liposome co-sedimentation is completely abolished in S165A LPLA2 mutant, while co-sedimentation of PLA2G15 coupled to IDFP or MAFP correlates with the length of their aliphatic chains. The error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent experiments. (** 0.001<p<0.01, ***p<0.001. na, not assayed due to poor protein expression; Student’s t-test)