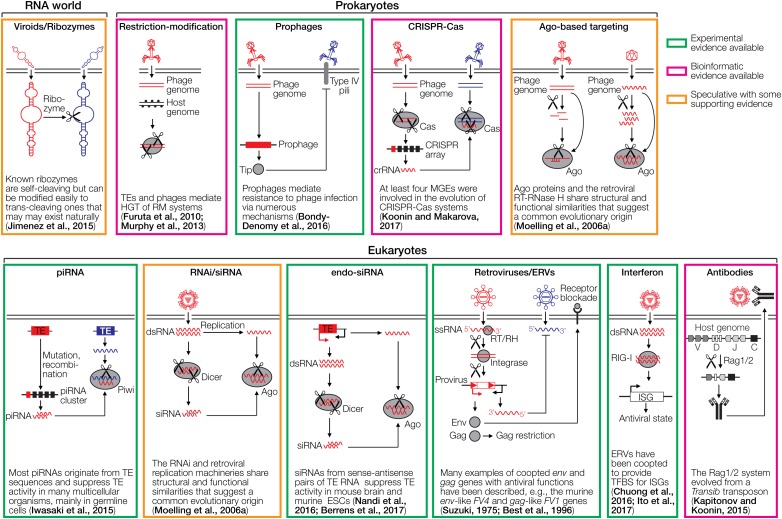
FIGURE 1.
Cartoons depicting various defense systems. The systems are color-coded based on the level of support in green (experimental evidence available), magenta (bioinformatic evidence available), and orange (speculative with some supporting evidence). DNA/RNA cleaving is indicated with scissors. RNA is depicted as wavy lines or with secondary hairpin-loop structures. A ribozyme cleaving another ribozyme is a hypothetical early immune system that does not require DNA or proteins. The ribozyme may be part of a viroid-like selfish RNA. Restriction-modification systems distinguish between foreign and self DNA by methylating target sequences of restriction endonucleases. Prophages can mediate superinfection exclusion, exemplified by expression of the Tip protein that reduces bacterial surface expression of type IV pili required for infection by various phages. CRISPR-Cas acts by incorporating small genomic fragments from phages into CRISPR arrays in the prokaryotic genome. The transcribed spacers are then used by another Cas member to cleave sequence-homologous phage genomes. PIWI-associated RNAs (piRNAs) are small RNAs complementary to transposable elements (TEs) that are encoded in piRNA clusters (Iwasaki et al., 2015). piRNAs associate with a PIWI nuclease to cleave complementary TE transcripts. RNA interference (RNAi) is initiated by dsRNA which is fragmented by Dicer to siRNAs. These siRNAs are loaded into the RNA-induced silencing complex to cleave complementary RNAs using Ago nucleases. A variation of RNAi is the endo-siRNA pathway, in which dsRNA is generated from TEs that are transcribed in both orientations, for instance, if the TE is located in an intron in opposite orientation to the encompassing gene. Endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) can mediate restriction of ERVs and exogenous retroviruses through various mechanisms, including receptor blockade by captured Env proteins, Gag-mediated restriction and antisense RNA mechanisms. The interferon system recognizes dsRNA or other pathogen-associated molecular patterns, which leads to upregulation of antiviral interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs). The antibody system involves diversification through light and heavy chain recombination, which is mediated by the Rag recombinases. This enables the detection of diverse pathogens. Note that the references provided in the figure are not comprehensive. Please refer to the text for more details and additional references.