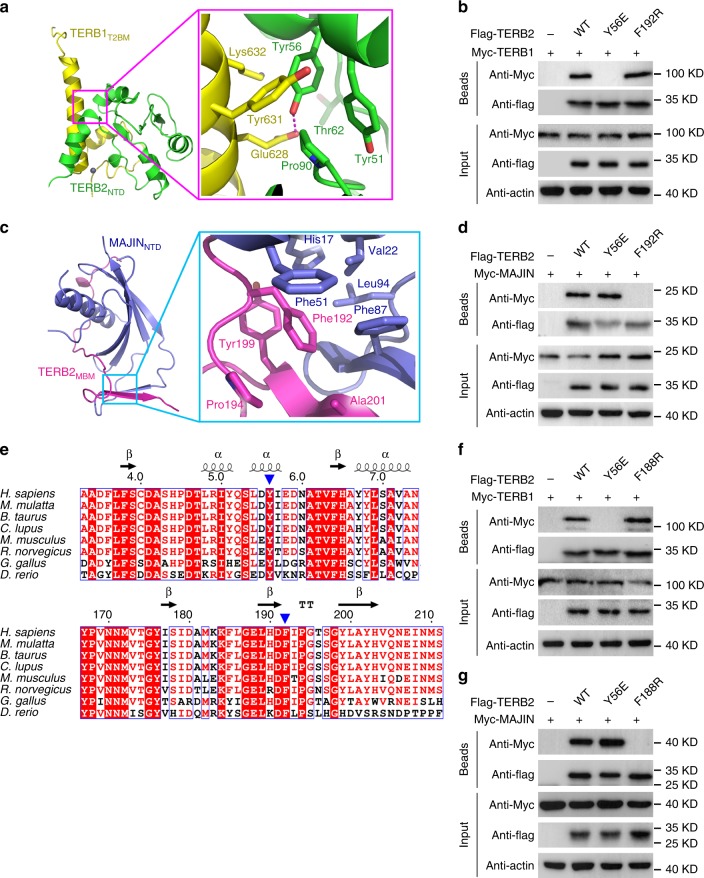
Fig. 4.
Mutational analyses of the TERB1–TERB2 and TERB2–MAJIN interactions. a, c Detailed interactions around Tyr56TERB2 in the TERB1T2BM–TERB2NTD complex (a) and around Phe192TERB2 in the TERB2MBM–MAJINNTD complex (c). b, d Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) of human TERB1 (b) or MAJIN (d) with wild-type (WT) or mutant Flag-tagged human TERB2 in 293T cells. The levels of each protein in the input and IP samples were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Input contains 5% of the input whole-cell lysate used for IPs. e Multiple sequence alignment of the N-terminal (top) and C-terminal (bottom) regions of TERB2 required for its association with TERB1 and MAJIN, respectively. Sequence positions are shown based on the human TERB2. The residues of Tyr56 (Try56 in mouse) and Phe192 (Phe188 in mouse) are indicated by blue arrowheads. f, g Co-IP of mouse TERB1 (f) or mouse MAJIN (g) with WT or mutant Flag-tagged mouse TERB2 in 293T cells. The levels of each protein in the input and IP samples were analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Input contains 5% of the input whole-cell lysate used for IPs. Source data are provided as a Source Data file