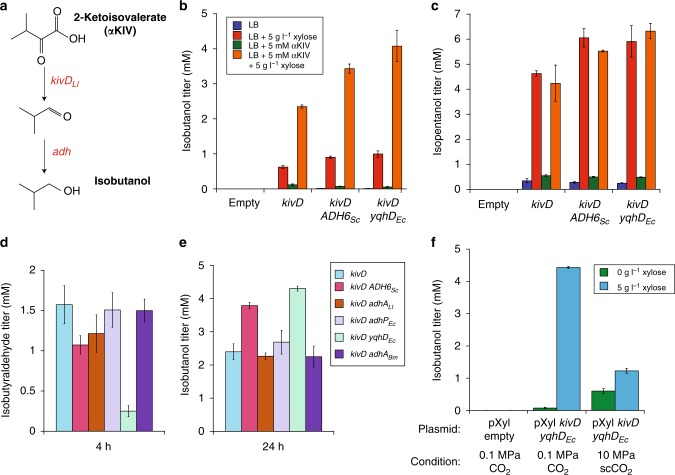
Fig. 4.
Isobutanol and isopentanol production in SR7. a Two-step enzyme pathway to convert the valine intermediate 2-ketoisovalerate (αKIV) to isobutanol using the decarboxylase enzyme KivD from L. lactis and an alcohol dehydrogenase. b Evaluation of isobutanol production at 24 h post induction in SR7 with an empty pXyl plasmid, pXyl kivD, pXyl kivD ADH6Sc, or pXyl kivD yqhDEc, where ADH6 and YqhD are alcohol dehydrogenases from S. cerevisiae and E. coli, respectively. Cultures were grown aerobically in LB medium in the presence and absence of 5 g l–1 xylose as an inducer and 5 mM αKIV as substrate for the pathway. For all aerobic experiments, error bars represent the standard deviation of biological triplicate cultures. c Co-production of isopentanol measured in SR7 samples shown in b. d Accumulation of the isobutyraldehyde intermediate at short culture times, 4 h post induction. Alcohol dehydrogenases ADH6 from S. cerevisiae, AdhA from L. lactis, AdhP from E. coli, YqhD from E. coli, and AdhA from B. megaterium SR7 were evaluated to decrease the buildup of isobutyraldehyde intermediate for aerobic cultures fed 5 mM αKIV and induced with xylose. e Production of isobutanol at 24 h post induction for the cultures shown in d. f Production of isobutanol for SR7 cultures grown under 0.1 MPa CO2 (biological triplicate cultures) and 10 MPa scCO2 at 37 °C. Under scCO2, cultures with at least a tenfold increase in cell number, as enumerated by microscopy, were analyzed for alcohol production, sugar consumption and fermentation product generation. Average isobutanol titers from the aqueous phase of cultures showing at least 1 mM glucose consumption (classified as high activity; Supplementary Fig. 11) are provided. Source data are provided as a Source Data file