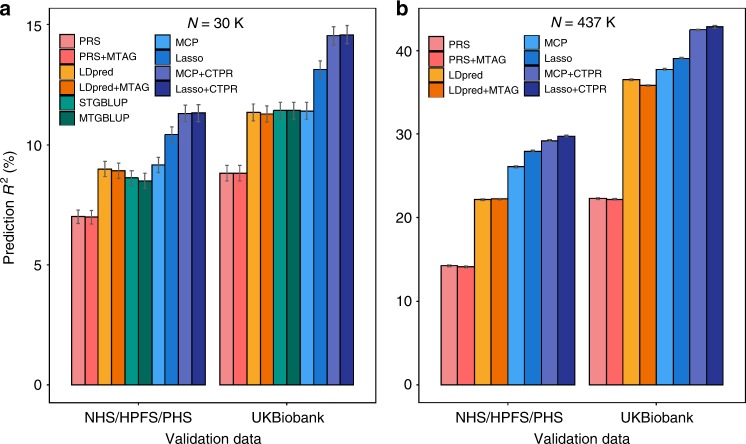
Fig. 3.
Comparisons of the predictive performance for HGT by the aid of BMI among LDpred, MTAG, STGBLUP, MTGBLUP, and CTPR using UK Biobank data (N = 30K or 437K) as a training set and either UK Biobank (N = 20K) or NHS/HPFS/PHS cohort (N = 20K) as a validation set. We considered human height (HGT) as the primary trait and body mass index (BMI) as the secondary trait. Prediction R2 were computed with two different validation sets (UK Biobank, NHS/HPFS/PHS data) and two different training sample sizes (30K, 437K) using summary-based prediction methods (LDpred, MTAG), GBLUP (STGBLUP, MTGBLUP), and the proposed prediction methods (MCP/MCP + CTPR, Lasso/Lasso + CTPR). Clearly, our multi-trait methods (Lasso + CTPR, MCP + CTPR) generated better predictive performance than our single-trait methods and the existing prediction methods with different training sample sizes and different validation sets. All error bars represent standard errors of prediction R2. a Real GWAS analysis results with 30K training samples for prediction R2 of HGT by the aid of BMI. b Real GWAS analysis results with 437K training samples for prediction R2 of HGT by the aid of BMI