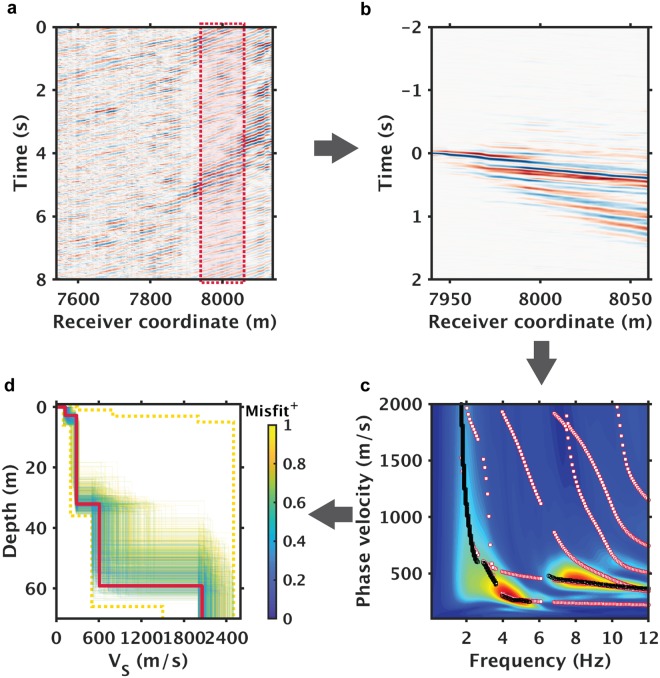
Figure 2.
Illustration of data processing workflow for ambient noise interferometry. (a) Example of train noise shown via an 8 second time domain slice. The red box in (a) highlights subsection of the array used for (b) noise correlation gather, (c) dispersion analysis, and (d) inversion of the shear-wave velocity (VS) profiles. Black and white markers in (c) denote observed and model-predicted multimodal dispersion curves respectively. In (d), the yellow dashed lines denote upper and lower bounds of the parameter space used in Monte Carlo sampling; the bold red line marks the best-fit VS profile; the yellow/blue lines denote the top 0.1% best-fitting VS profiles (color coded by their corresponding inversion misfits); Misfit† denotes normalized misfit values (min-max normalized by misfits of the top 0.1% VS profiles).