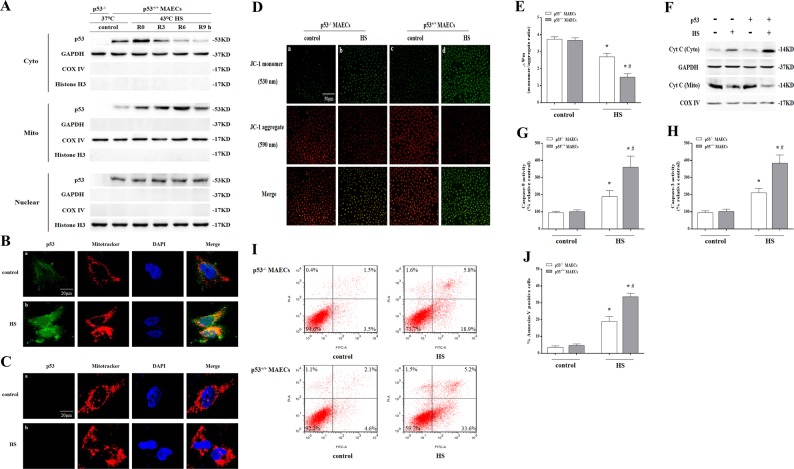
Fig. 1. Localization of p53 to the mitochondria played an essential role in mediating heat stress (HS)-induced apoptosis in p53+/+ mouse aortic endothelial cells (MAECs).
Both p53+/+ and p53-/- MAECs were isolated from wild-type and p53KO mice, respectively. a The p53+/+ MAECs were exposed to intense HS (43 °C) for 2 h and then incubated at 37 °C for the indicated durations of 0, 3, 6, or 9 h. The levels of p53 protein in the mitochondrial, cytosolic, and the nuclear fractions were assessed by western blot. GAPDH, cytosolic loading control; COX IV, mitochondrial loading control; Histone H3, nuclear loading control. The p53-/- and p53+/+ MAECs were exposed to 43 °C for 2 h and then incubated at 37 °C for 6 h (b–j). b–c Confocal laser scanning microscopy revealed localization of p53 to the mitochondria upon HS. Green fluorescence represents p53, red fluorescence represents Mito Tracker, and orange fluorescence represents translocation of p53 from the cytoplasm to the mitochondria. d Confocal laser scanning microscopy revealed localization of JC-1 aggregates and monomers in the cells. Green fluorescence represents JC-1 monomers and red fluorescence represents JC-1 aggregates. e Quantification of mitochondrial membrane potential changes (JC-1 monomer/JC-1 aggregates). f Cyt C protein levels in the mitochondrial and cytosolic fractions were assessed by western blot. g Enzymatic activity of Caspase-9 was measured using fluorogenic substrate Ac-LEHD-AFC. h Enzymatic activity of Caspase-3 was measured using fluorogenic substrate Ac-DEVD-AMC. i Apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry using Annexin V-FITC/PI staining. j Quantification of apoptosis induced by HS. *P < 0.05 compared with the control group (37 °C); #P < 0.05 compared with the HS group of p53-/- MAECs