Figure 5.
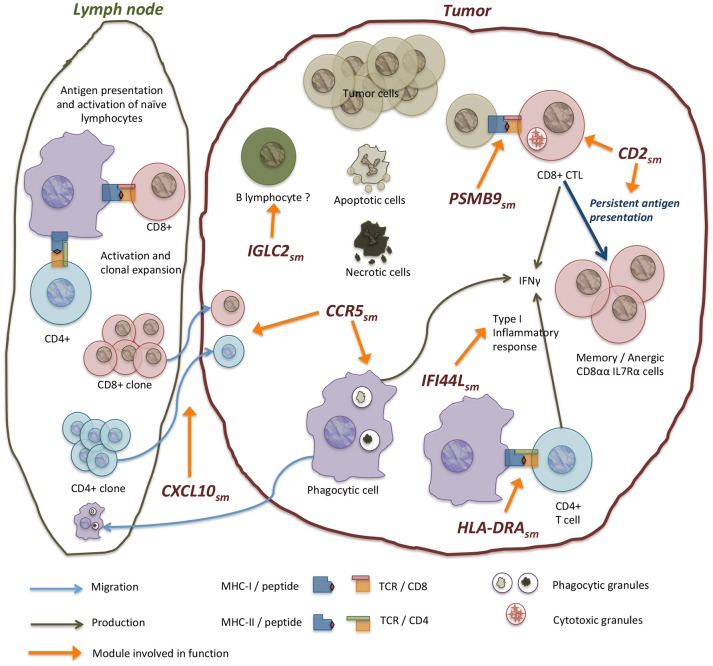
Modules in the network are enriched in processes of complementary biological functions. CCR5sm contains genes involved in antigen acquisition via receptor mediated phagocytosis, endosome components, as well as a number of chemokines that mediate immune cell recruitment. PSMB9sm contains genes of components of the immunoproteasome and MHC-I molecules involved in the presentation of internally produced antigens. The immunoproteasome is induced by IFNγ signaling and is associated with a response to intracellular infections and transformation in tumor cells. HLA−DRAsm contains MHC-II genes involved in antigen presentation to CD4+ T lymphocytes. Other modules like IFI44Lsm also contain interferon-induced genes annotated with antiviral functions. CD2sm has genes involved in T lymphocyte function, including T cell receptor components and co-receptor molecule CD8A as well as other genes related to T cell cytotoxic function like perforin and granzymes. Inside tumors, antitumor mechanisms coexist with tolerance mechanisms which impair tumor immune destruction. Our results suggest an active process of tolerance where cytotoxic CD8+ lymphocytes turn to anergic/memory cells that no longer fight the tumor. This is supported by the coregulation of CD8A and IL7R genes in CD2sm but not of CD8B. Other modules like IGLC2sm contain genes of immunoglobulin chains, including constant and variable chains that may be indicative of the presence of B lymphocyte infiltrates.