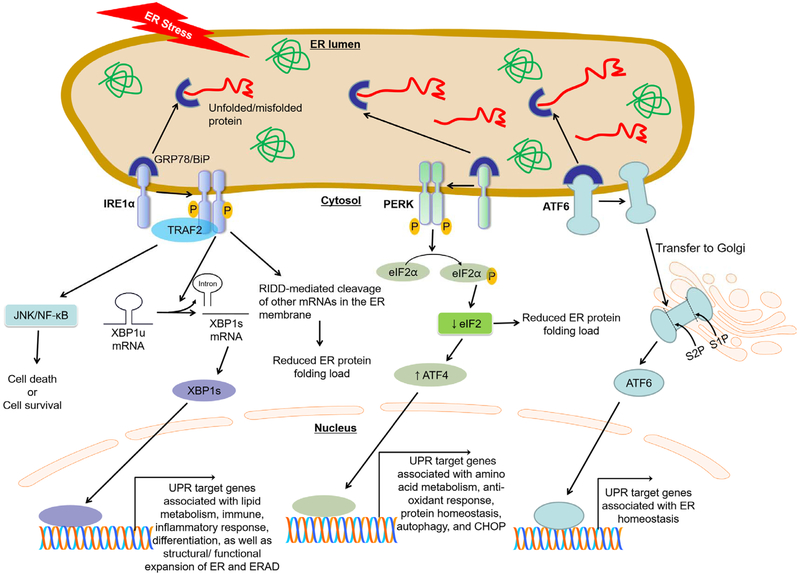
Fig. 1. The three branches of the unfolded protein response (UPR).
In unstressed conditions, stress sensor proteins activating transcription factor (ATF) 6, inositol-requiring enzyme (IRE1) α, and RNA-dependent protein kinase-like ER-resident kinase (PERK), representing the three branches of the UPR, are associated with the folding chaperone glucose regulated protein/binding immunoglobulin protein (GRP78/BiP) in the ER. Accumulation of unfolded/misfolded proteins within the ER lumen causes GRP78/BiP disassociation from these three sensor proteins, leading to UPR activation. Each pathway uses a different mechanism of signal transduction. Activated IRE1α mediates unconventional splicing of X-box binding protein (XBP) 1 to produce spliced, active isoform of XBP1. IRE1α recruits TNF receptor associated factor (TRAF) 2 to activate the downstream signal mediators, NF-κB/JNK. IRE1α-mediated activations of XBP1 and TRAF2/NF-κB/JNK regulate UPR target genes associated with lipid metabolism, immune, inflammatory response, and differentiation, as well as structural/ functional expansion of ER and ER-associated protein degradation (ERAD). In addition, IRE1α can reduce the ER protein folding load by the IRE1-dependent decay of mRNA (RIDD) causing degradation of ER membrane-bound mRNAs. Activated PERK recruits and phosphorylates eukaryotic initiation factor (eIF2) α reduce global protein synthesis and thereby reduce protein folding load in ER-stressed cells. Paradoxically, however, PERK/eIF2α-translation of ATF4 increases certain UPR gene transcriptions, including CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein homologous protein (CHOP). Lastly, activated ATF6 is exported to the Golgi apparatus where it is cleaved by the Golgi-resident proteases SP1 and SP2 to produce the functional fragment of ATF6. The functional ATF6 is then translocated to the nucleus where it transactivates UPR genes associated with ER homeostasis.