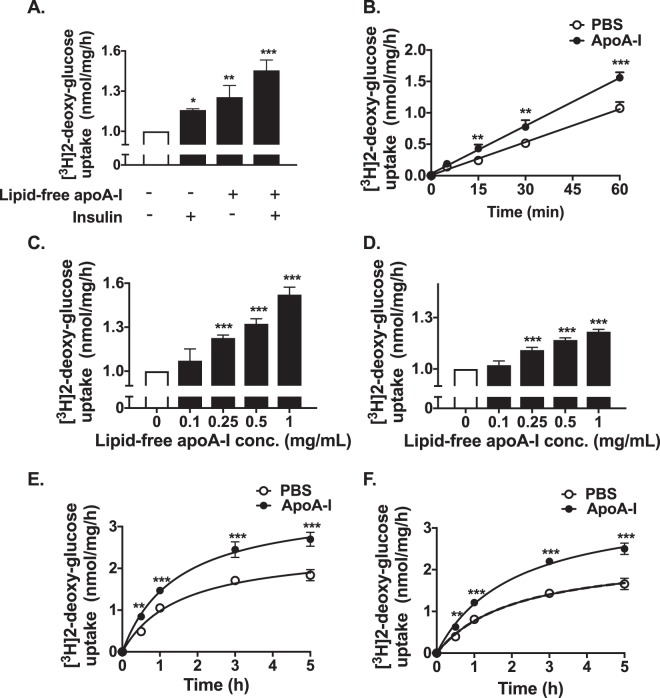
Figure 1.
ApoA-I increases glucose uptake into HSKMCs. (A) HSKMCs were incubated at 37 °C for 16 h in serum-free MEM-α with or without apoA-I (1 mg/mL final concentration). The apoA-I was removed and the cells were incubated at 37 °C for 1 h with or without insulin (0.1 µmol/L final concentration). (B) Glucose uptake was assessed from 5 to 60 min in HSKMCs pre-incubated with (closed symbols) or without (open symbols) apoA-I as in Panel A, then incubated for a further 1 h in the presence of insulin (0.1 µmol/L final concentration). (C,D) HSKMCs were incubated at 37 °C for 16 h in serum-free MEM-α with or without apoA-I (0.1–1 mg/mL final concentration). The apoA-I was removed, and the cells were incubated for 1 h in the (C) presence or (D) absence of insulin (0.1 µmol/L final concentration). (E,F) Glucose uptake was assessed from 0.5 to 5 h in HSKMCs pre-incubated with (closed symbols) or without (open symbols) apoA-I as in Panel A, then incubated for a further 1 h in the (E) presence or (F) absence of insulin (0.1 µmol/L final concentration). Glucose uptake was determined as described in Materials and Methods. Values represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Glucose uptake was normalized to 1 nmol/mg/h for cells incubated under basal conditions (open bar, Panels A, C,D). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. control (open bars and circles).