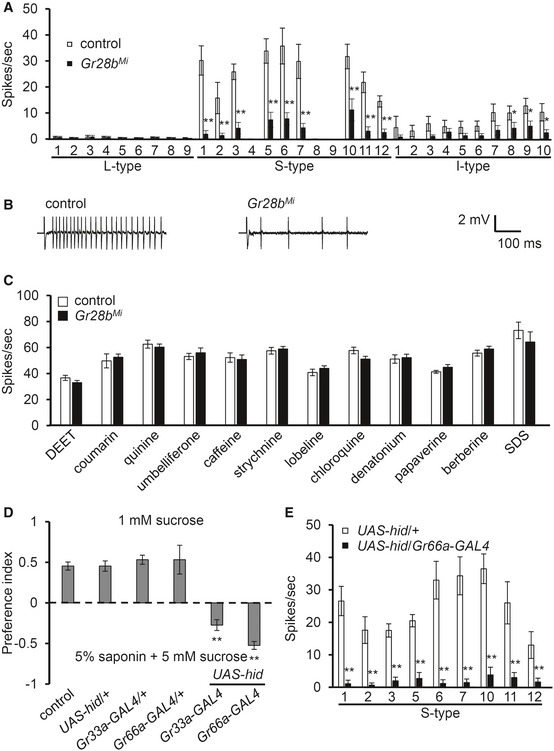
Mapping analysis of all the sensilla following stimulation with 5% saponin in control and Gr28b
Mi flies (we followed Tanimura's nomenclature) (n ≥ 8).
Sample traces of saponin‐induced action potentials on S6 sensilla.
Tip recording analysis of S6 sensilla from control and Gr28b
Mi flies. Stimuli used are 0.2% DEET, 1.0 mM coumarin, 0.5 mM quinine, 10 mM umbelliferone, 10 mM caffeine, 0.3 mM strychnine, 0.3 mM lobeline, 0.1 mM chloroquine, 0.2 mM denatonium, 0.5 mM papaverine, 0.1 mM berberine, and 0.1% SDS (n ≥ 7).
Binary food choice assays were conducted after GRNs were ablated by expressing the cell death gene (hid), under Gr33a‐GAL4 or Gr66a‐GAL4. All heterozygote controls (UAS‐hid/+, Gr33a‐GAL4/+, and Gr66a‐GAL4/+) are shown (n ≥ 4).
Tip recording analysis of the indicated S‐type sensilla and genotypes (n ≥ 7).
Data information: The error bars represent SEMs. The asterisks indicate significant differences from that of the control detected by a single‐factor ANOVA with Scheffe's analysis as a
< 0.01).