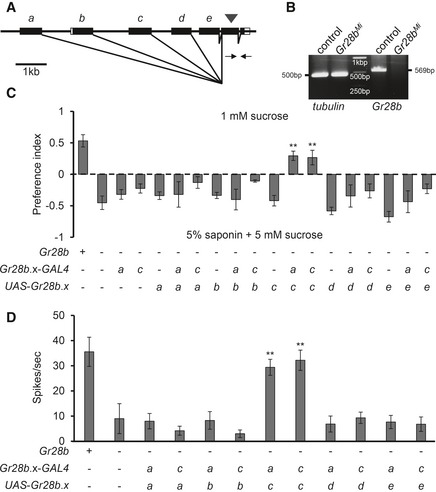
Figure 4. The structure of Gr28b genome and specific requirement of GR28b(C) for saponin‐mediated avoidance and electrophysiology.
-
AThe genomic structure of Gr28b. It is composed of five different forms by alternative splicing. The arrowhead indicates the P‐element insertion. White boxes indicate predicted untranslated regions in flybase. Arrows indicate primers for RT–PCR.
-
BRT–PCR analysis with the indicated primers in (A) for control and Gr28b Mi flies with tubulin as a control. From left to right, the band of tubulin of wild‐type, tubulin of Gr28b Mi, DNA ladder, Gr28b of wild‐type, and Gr28b of Gr28b Mi flies.
-
C, DEach isoform from Gr28b.a to Gr28b.e was driven by Gr28b.a‐GAL4 or Gr28b.c‐GAL4 in a Gr28b Mi background. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). The asterisks indicate significant differences from that of the Gr28b mutant detected by a single‐factor ANOVA with Scheffe's analysis as a post hoc test to compare two sets of data (**P < 0.01). (C) Binary food choice assay for recovery experiments with each of the five alternative Gr28b isoforms using the GAL4/UAS systems (n ≥ 4). (D) Saponin‐induced action potential frequencies from the indicated transgenic flies on S6 sensilla (n = 7).
