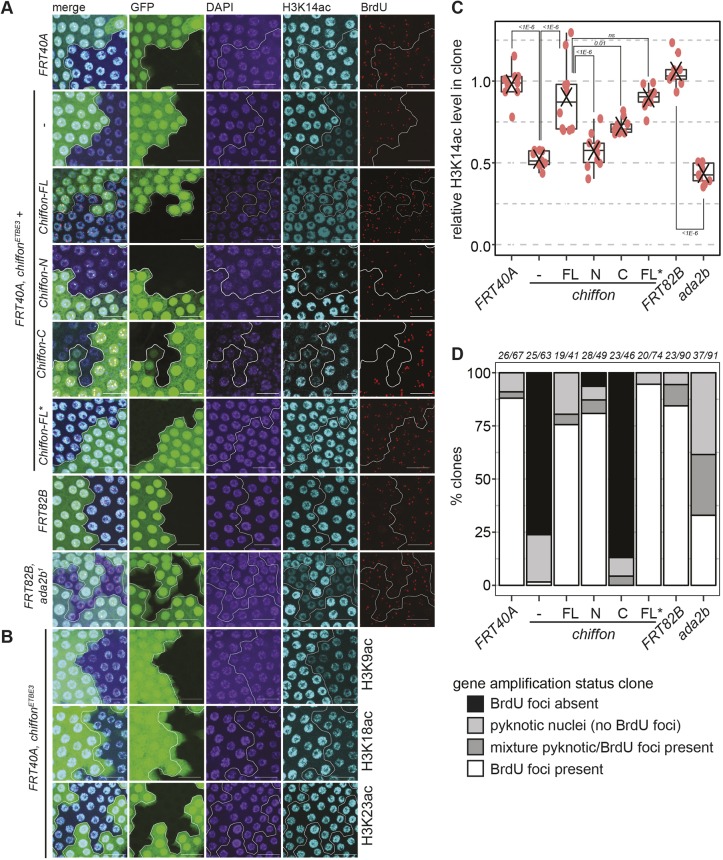
Fig. 4.
Chiffon is necessary for histone H3 acetylation in vivo. (A) Mosaic egg chambers were generated using the FLP/FRT system for chiffonETBE3 and ada2b1, their respective controls, FRT40A and FRT82B, and for chiffonETBE3 clones expressing single copies of the indicated Chiffon rescue transgenes. Maximum-intensity projection images showing BrdU incorporation, α-H3K14ac and DAPI staining from amplification-stage egg chamber follicle cells containing representative clones, marked by the absence of GFP and outlined in white. Scale bars: 20 µm. (B) Mosaic egg chambers for chiffonETBE3 were examined for H3K9ac (n=5), H3K18ac (n=6) or H3K23ac (n=7) as in A. Representative images are shown for each histone modification. Scale bars: 20 µm. (C) Box plots showing relative H3K14ac levels in mutant clones versus GFP-positive control regions. 10–30 nuclei were quantified per region for 9–10 independent animals (red dots indicate clone analyzed from an individual animal; X, mean). P-values for the indicated comparisons were determined by ANOVA+Tukey-HSD; ns, not significant. (D) The percentage of clones undergoing gene amplification (BrdU-positive foci) in amplification-stage egg chambers from the indicated genotypes was determined. Several genotypes showed clones that were composed entirely or partially of pyknotic nuclei, which did not undergo gene amplification. The number of independent animals and clones examined for each genotype is shown above the plot (animals/clones).